题目
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4) Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
注意
这题因为没有限定数字可以有多长,所以转型成int,long或者BigDecimal计算的方法都失败了。
朴素解法
短的那个数字,不足的位用0补足。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(-1); // HEAD
ListNode index = result;
int carry = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
while (true) {
if (l1 == null && l2 == null) {
if (carry == 1) {
ListNode next = new ListNode(carry);
index.next = next;
}
return result.next;
}
if (l1 != null) {
num1 = l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
num1 = 0;
}
if (l2 != null) {
num2 = l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
} else {
num2 = 0;
}
int sum = num1 + num2 + carry;
index.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
index = index.next;
carry = sum / 10;
}
}
}
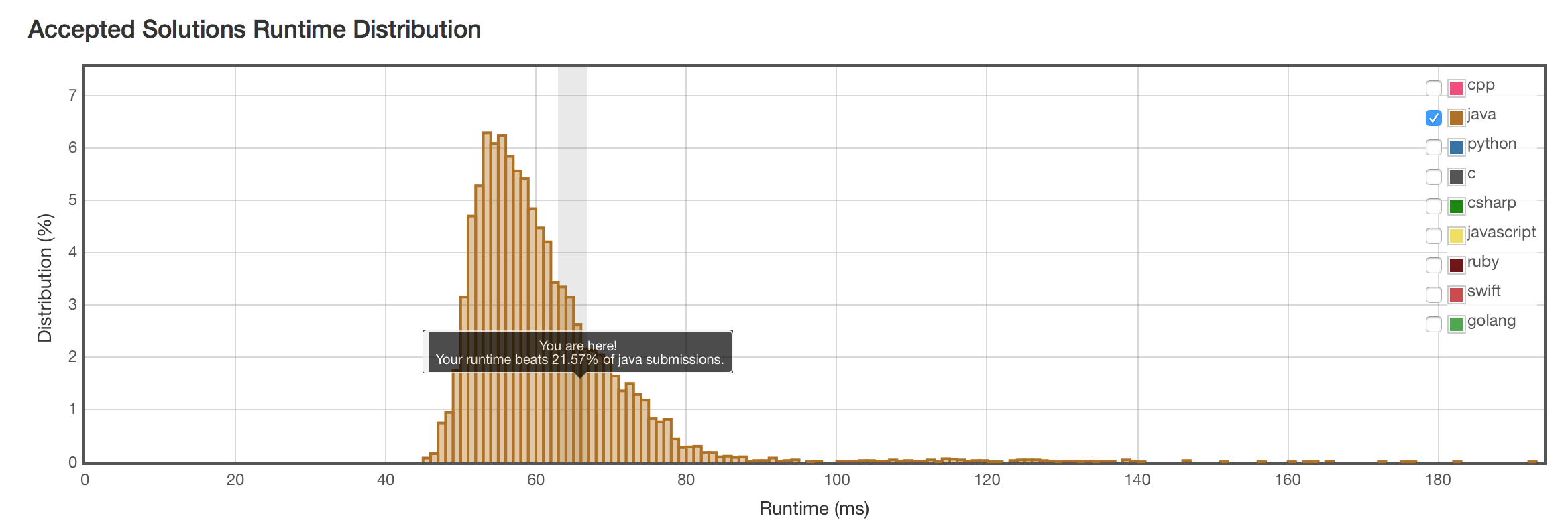
结果
优化两个数长度不相等的情况(递归版)
当一个数比另一个数更长,后半部分的加法就不用做,只是进了一位,或者直接照搬。
这个版本的缺点是,逻辑太复杂。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1.val == 0 && l1.next == null) { // base case l1 = 0
return l2;
}
if (l2.val == 0 && l2.next == null) { // base case l2 = 0
return l1;
}
ListNode result = new ListNode(-1); // HEAD is not included in the result
ListNode index = result;
int carry = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
if (l2.val == 1 && l2.next == null) { // base case l2 = 1
while (l1 != null && l1.val == 9) {
index.next = new ListNode(0);
l1 = l1.next;
index = index.next;
carry = 1;
}
if (l1 == null) {
index.next = new ListNode(1);
} else {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(l1.val + 1);
newNode.next = l1.next;
index.next = newNode;
}
return result.next;
}
while (true) {
if (l1 == null && l2 == null) {
if (carry == 1) {
ListNode next = new ListNode(carry);
index.next = next;
}
return result.next;
}
if (l1 == null) { // l2更长,递归
index.next = addTwoNumbers(l2,new ListNode(carry));
return result.next;
}
if (l2 == null) { // l1更长,递归
index.next = addTwoNumbers(l1,new ListNode(carry));
return result.next;
}
// add two numbers on this bit, normal case
int sum = l1.val + l2.val + carry;
l1 = l1.next;
l2 = l2.next;
index.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
index = index.next;
carry = sum / 10;
}
}
}
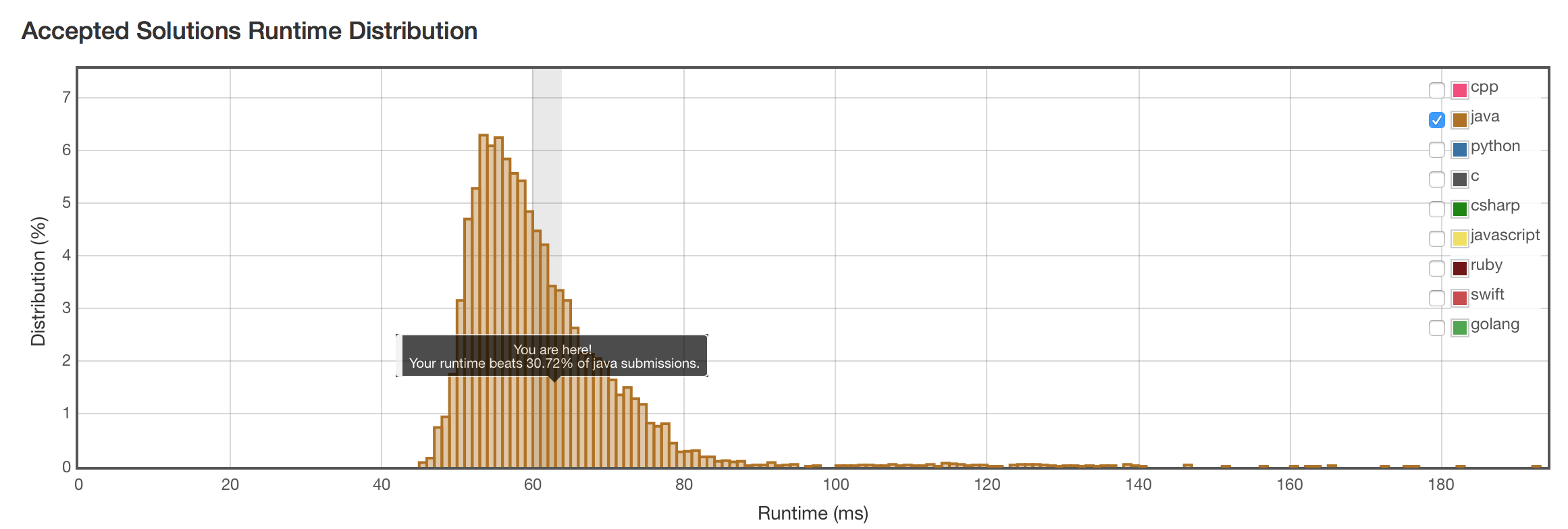
结果
虽然理论上当两个数字长度相差很大的时候,应该有所优化。但实际测试效果不理想,还不如朴素方法。