题目
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Examples:
Given abcabcbb, the answer is abc, which the length is 3.
Given bbbbb, the answer is b, with the length of 1.
Given pwwkew, the answer is wke, with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a substring, pwke is a subsequence and not a substring.
朴素解法
老老实实从第一个字符开始,两层迭代。需要额外维护一个容器,来检查字符是否重复。朴素解法通过了所有测试,但是超时。
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Set<Character> charSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
int maxSize = 0;
outerIter:
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (chars.length - i < maxSize) { break; } // 剩下的字符串比maxSize小,停止遍历
innerIter:
for (int j = i; j < chars.length; j++) {
if (charSet.contains(chars[j])) {
if (charSet.size() > maxSize) {
maxSize = charSet.size();
}
charSet.clear();
break innerIter;
}
charSet.add(chars[j]);
}
if (charSet.size() > maxSize) {
maxSize = charSet.size();
}
charSet.clear();
}
return maxSize;
}
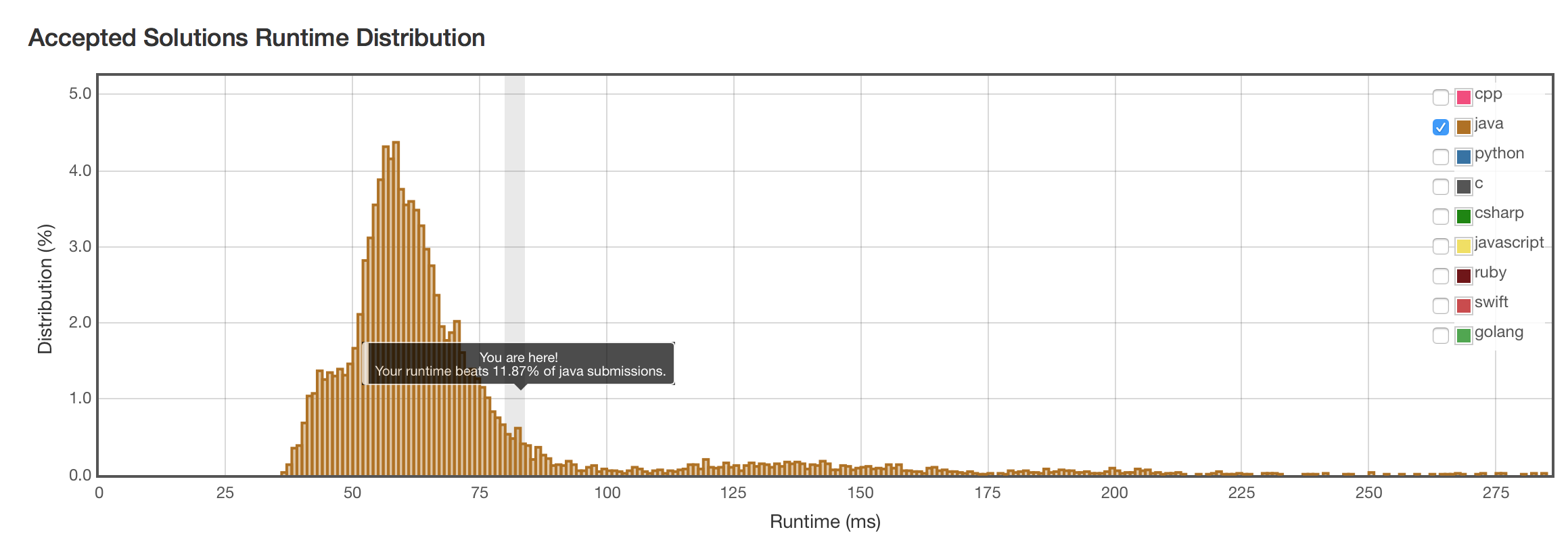
结果
通过了所有测试,但是超时。
改进版:第二个指针不回头
因为预存到临时容器里的内容都是没有重复字符的。所以第二个指针没必要每次都回到第一个指针的位置重新遍历。只要丢弃掉容器里的第一个字符,第二个指针就可以从原地开始遍历。整体复杂度降低到线性的O(n)。
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Queue<Character> charQueue = new LinkedList<>();
int maxSize = 0;
int cursorJ = 0;
outerFor:
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
charQueue.poll(); // poll don't throw Exception if it's empty.
innerWhile:
while (true) {
if (cursorJ == chars.length) { // finish all work
break outerFor;
}
if (charQueue.contains(chars[cursorJ])) {
break innerWhile;
}
charQueue.offer(chars[cursorJ]);
cursorJ++;
}
if (charQueue.size() > maxSize) {
maxSize = charQueue.size();
}
}
if (charQueue.size() > maxSize) {
maxSize = charQueue.size();
}
return maxSize;
}
}
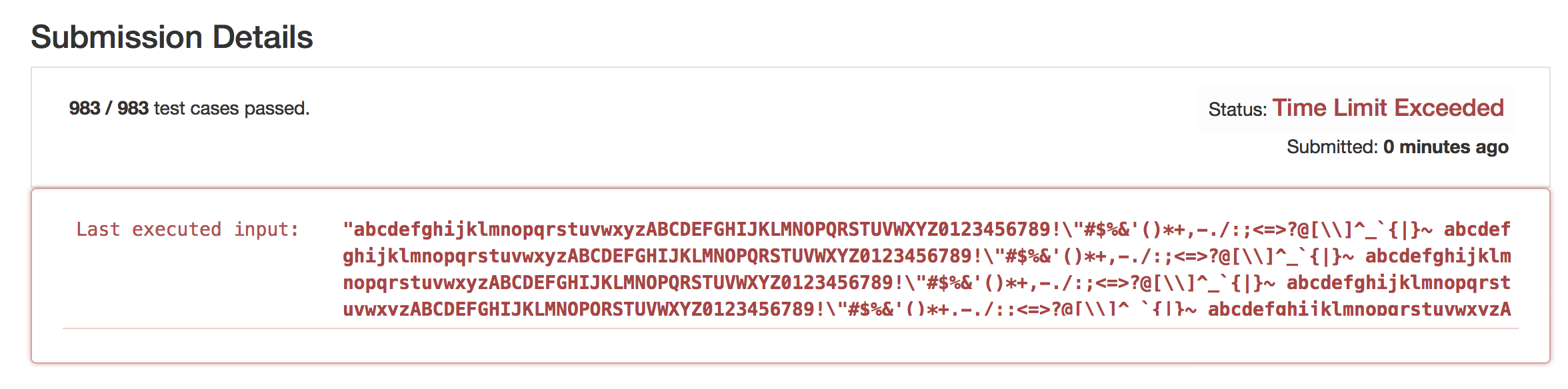
结果
再改进版:第一个指针跳过重复字符前的所有字符
因为重复字符之前的所有字符都没必要遍历了,可以直接跳过。
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
LinkedList<Character> charQueue = new LinkedList<>();
int maxSize = 0;
int cursorJ = 0;
outerFor:
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
charQueue.poll(); // poll don't throw Exception if it's empty.
int offset = 0; //重复字符在LinkedList里的偏移值
innerWhile:
while (true) {
if (cursorJ == chars.length) { // 出口1,遍历完成,结束所有工作
break outerFor;
}
if (charQueue.contains(chars[cursorJ])) { // 出口2,出现重复字符
offset = charQueue.indexOf(chars[cursorJ]); // 跳过重复字符前的所有字符
break innerWhile;
}
charQueue.offer(chars[cursorJ]);
cursorJ++;
}
if (charQueue.size() > maxSize) { // 每次循环之后结算
maxSize = charQueue.size();
}
// 2号出口出来到这里。跳过重复字符之前的所有字符
if (offset > 0) {
i += offset;
for (int x =0; x < offset; x++) {
charQueue.poll();
}
}
}
// 1号出口出来到这里。
if (charQueue.size() > maxSize) { // 返回前再结算一次。
maxSize = charQueue.size();
}
return maxSize;
}
}
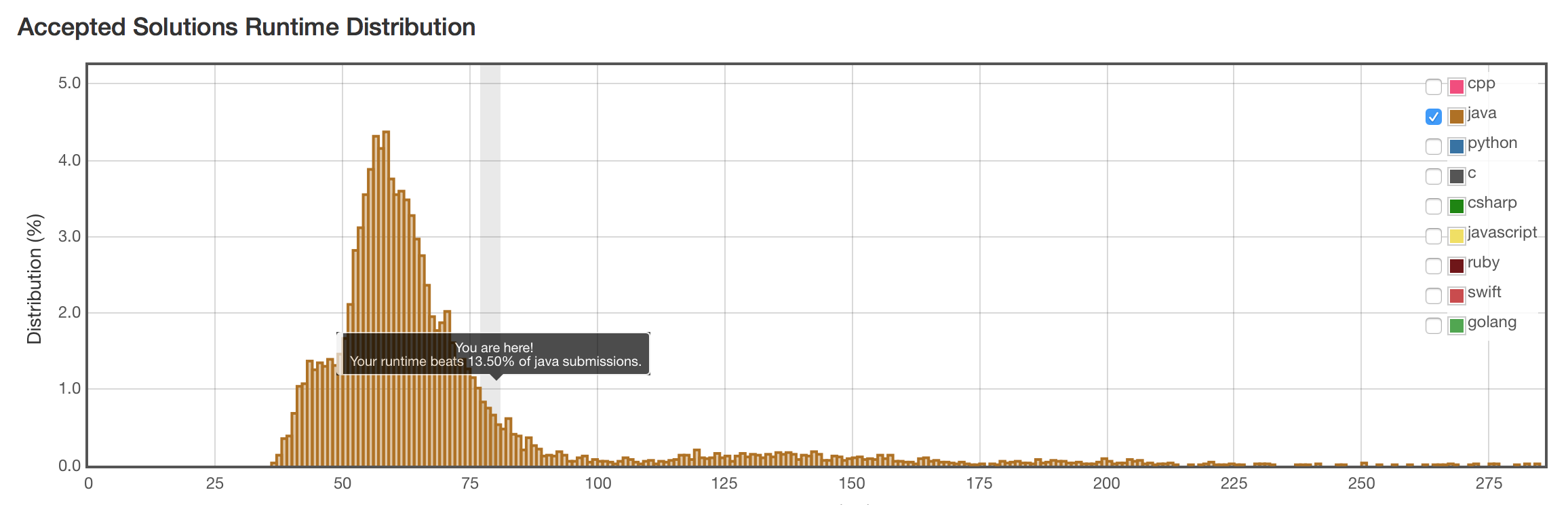
结果
最终版
综合考虑逻辑复杂性和性能的话,还是第二个算法最简洁且高效。以下是第二种算法的简化版代码。逻辑很清楚。
public class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int fastCursor = 0;
int slowCursor = 0;
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
int max = 0;
while (fastCursor < s.length()) {
if (!set.contains(s.charAt(fastCursor))) {
set.add(s.charAt(fastCursor++));
max = Math.max(max,set.size());
} else {
set.remove(s.charAt(slowCursor++));
}
}
return max;
}
}
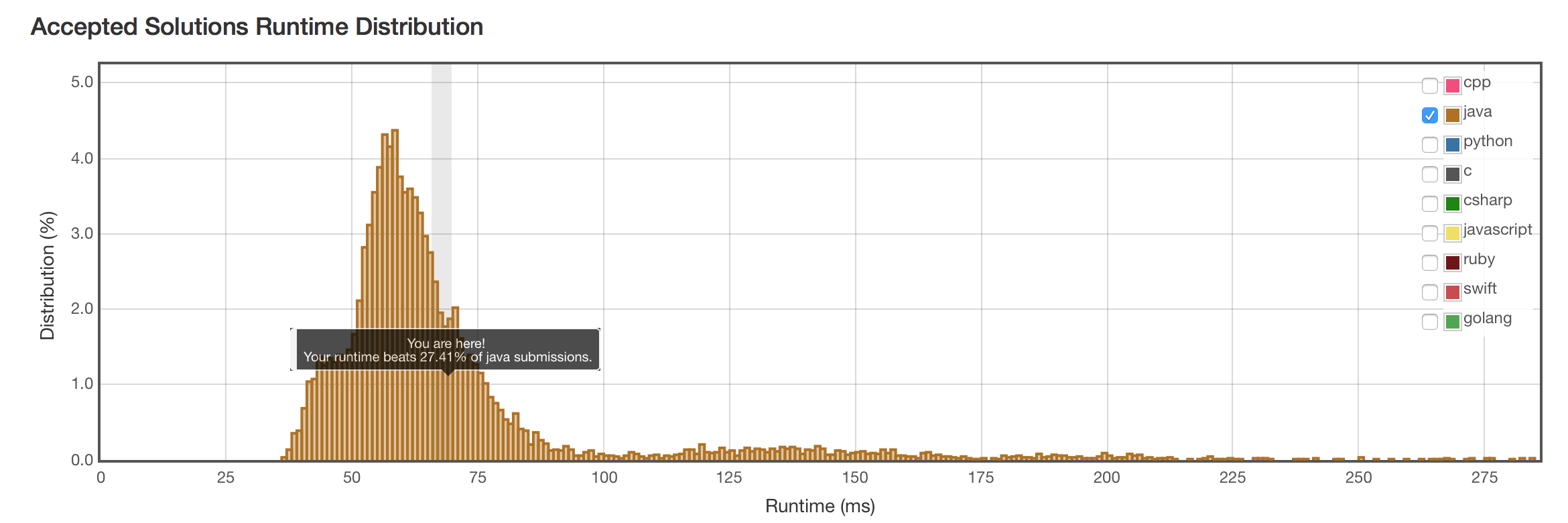
结果
虽然结果不是最高效,但已经是O(n)的复杂度。对它的其他优化效果不明显,而且代码逻辑会很复杂,不值得。