主要收获
要打破单向遍历的思维习惯。在一个有序数列上,双向查找(bi-directional 2Sum sweep),也可以叫Two Pointers,的复杂度是\(O(n)\),比两层套嵌遍历的\(O(n^2)\)有效很多。
题目
Given an array S of n integers, are there elements a, b, c in S such that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
For example, given array S = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
暴力遍历 \(O(n^3)\)
这种题,暴力遍历都是同一个套路。但这题三层套嵌遍历,复杂度\(O(n^3)\)太高。而且,为了剔除重复的结果,还预先排序一次。
代码
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> rlt = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 3) { return rlt; }
forI:
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-2; i++) {
forJ:
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length-1; j++) {
forK:
for (int k = j+1; k < nums.length; k++) {
if ((nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k]) == 0) {
List<Integer> ele = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(new Integer[] {nums[i],nums[j],nums[k]}));
Collections.sort(ele);
innerFor:
for (List<Integer> list : rlt) { // eliminate duplicate
if (list.equals(ele)) { continue forK; }
}
rlt.add(ele);
}
}
}
}
return rlt;
}
}
结果
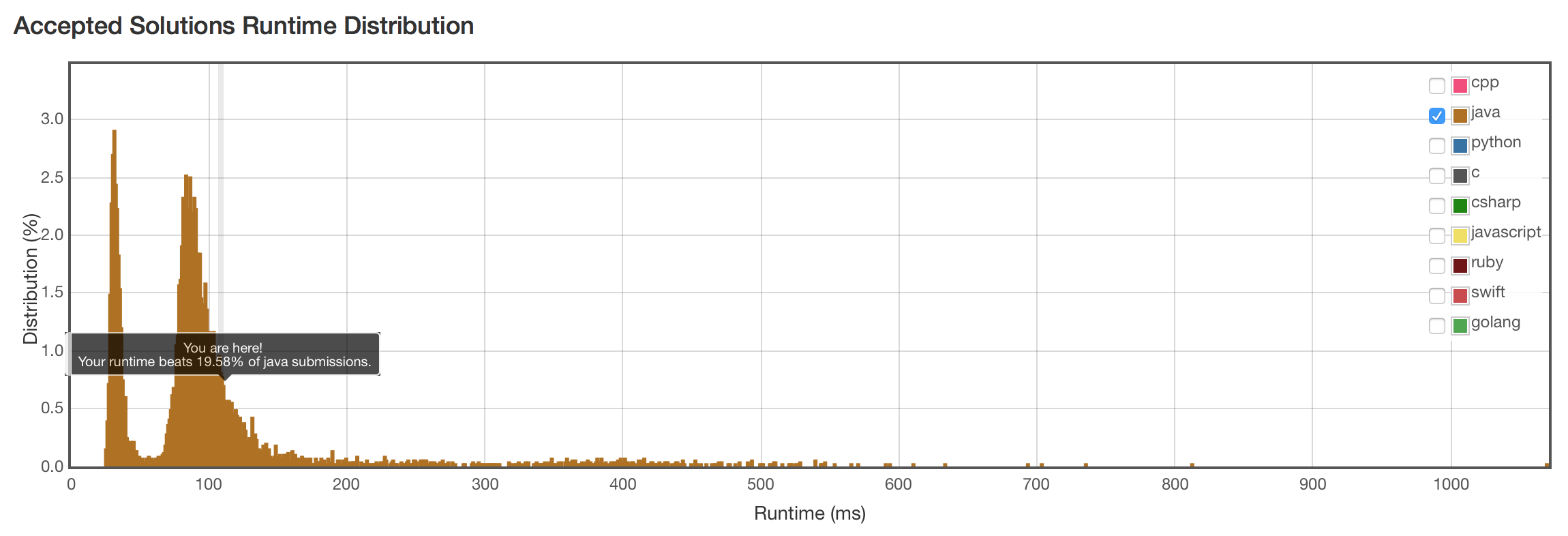
结果算法正确,超时了。
先排序,用前两个数去搜匹配的第三个数 \(O(n^3)\)
先排序,然后把数组分成两部分:小于零的,和大于等于零的。考虑这个数组:
[-4,-2,1,-5,-4,-4,4,-2,0,4,0,-2,3,1,-5,0]
排序以后像这样:
[-5, -5, -4, -4, -4, -2, -2, -2, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 3, 4, 4]
分为两个数组,然后只需要考虑从一个数组中取1个数,从另一个中取2个数的情况。
[-5, -5, -4, -4, -4, -2, -2, -2]
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 3, 4, 4]
因为Arrays没有类似contains()或者indexOf()函数,需要手动二分查找。
代码
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
Set<List<Integer>> rlt = new HashSet<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 3) { return new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(rlt); }
Arrays.sort(nums); // 排序
int firstPositive = firstPositive(nums); //找第一个大于等于0的数
// 处理特殊情况
if (firstPositive < nums.length-2 && nums[firstPositive] == 0 && nums[firstPositive+1] == 0 && nums[firstPositive+2] == 0) { // 存在0,0,0
rlt.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{0,0,0})));
}
if (firstPositive == 0 || firstPositive == nums.length) { // all >=0, or all <0
return new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(rlt);
}
// ready,go!
int negaSize = firstPositive;
int posSize = nums.length - firstPositive;
// searching by indexOf()
if (negaSize > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < negaSize-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < negaSize; j++) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j];
int index = indexOf(nums,firstPositive,nums.length-1,0-sum);
if (index != -1) { // find a new triplet
rlt.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{nums[i],nums[j],nums[index]})));
}
}
}
}
if (posSize > 1) {
for (int i = firstPositive; i < nums.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j];
int index = indexOf(nums,0,firstPositive-1,0-sum);
if (index != -1) { // find a new triplet
rlt.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{nums[i],nums[j],nums[index]})));
}
}
}
}
return new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(rlt);
}
// return the index of the first num >= 0
private int firstPositive(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= 0) { return i; }
}
return nums.length;
}
// 数组中二分查找一个数字(数组含左边界,含右边界)
// return index. or -1 if not found.
// 如果有多个数值相同,返回任意一个的index都可以。
private int indexOf(int[] nums, int low, int high, int num) {
if (low > high) { return -1; }
int median = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (nums[median] == num) {
return median;
} else if (nums[median] < num) {
return indexOf(nums,median+1,high,num);
} else { // nums[median] > num
return indexOf(nums,low,median-1,num);
}
}
}
结果
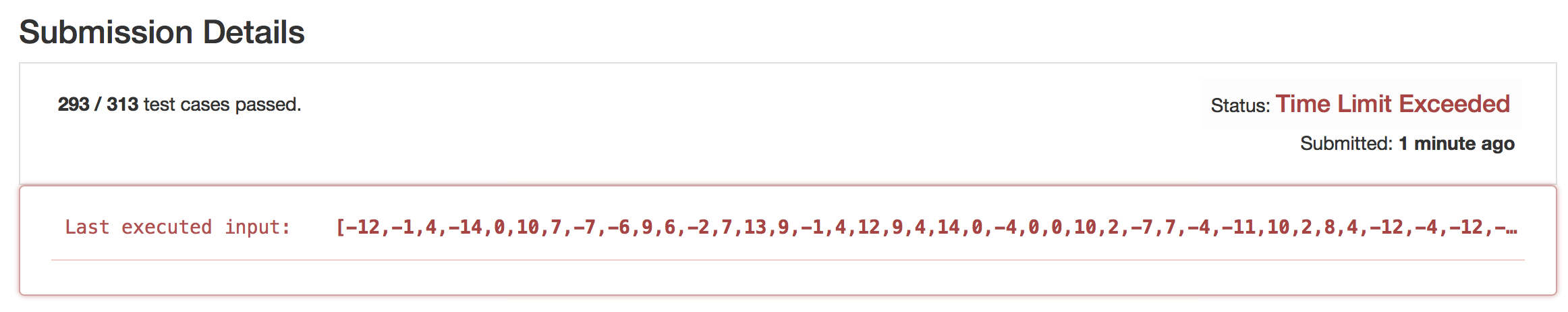
刚刚通过。但这不是银弹方法。
银弹!先排序,用第一个数字,双向查找后两个数字 \(O(n^2)\)
换一种思路,不用两层套嵌遍历。
数组先排序。遍历数组,获得第一个数,剩下两个数用双向查找,搜索和为一定值的两个数。查找过程,先在数组首尾分别设置一个指针。当两个指针指向的值的和小于第一个数的相反数,低位指针左移,否则,高位指针右移。
代码
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length < 3) { return result; }
Arrays.sort(nums);
int main = 0;
while (main < nums.length-2) {
if (nums[main] > 0) { break; }
int low = main + 1;
int high = nums.length-1;
while ( low < high ) {
long sum = (long)( nums[main] + nums[low] + nums[high] );
if (sum == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{nums[main],nums[low],nums[high]})));
}
if (sum <= 0) {
while (low+1 < high && nums[low] == nums[low+1]) { low++; }
low++;
}
if (sum >= 0) {
while (low < high-1 && nums[high] == nums[high-1]) { high--; }
high--;
}
}
while (main+1 < nums.length-2 && nums[main] == nums[main+1]) { main++; }
main++;
}
return result;
}
}
简洁版
用++,--简化了部分代码。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if(nums.length < 3) return result;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int i = 0;
while(i < nums.length - 2) {
if(nums[i] > 0) break;
int j = i + 1;
int k = nums.length - 1;
while(j < k) {
int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k];
if(sum == 0) result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]));
if(sum <= 0) while(nums[j] == nums[++j] && j < k);
if(sum >= 0) while(nums[k--] == nums[k] && j < k);
}
while(nums[i] == nums[++i] && i < nums.length - 2);
}
return result;
}
}
结果
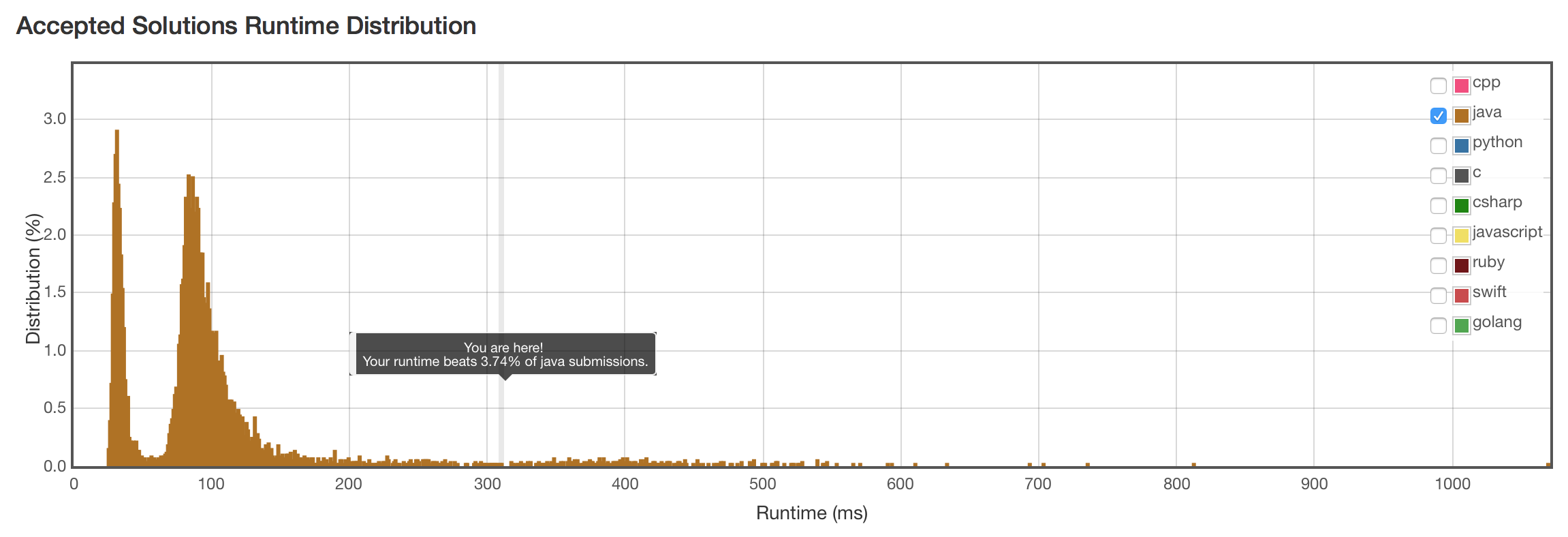
比\(O(n^3)\)的套嵌遍历快了一倍还多。结果还不理想,可能是服务器的原因。