题目
Given a string containing just the characters (, ), {, }, [ and ], determine if the input string is valid.
The brackets must close in the correct order, () and ()[]{} are all valid but “(]” and “([)]” are not.
用LIFO的Stack检查 \(O(n)\)
把符号分为左边符{[(和右边符)]}两组。遇到{[(就把他们存到Stack里,遇到)]}就peek出当前处于最上面的一个左边符,检查是否匹配。有3中失败的情况:
([)]:关闭的右边符和上一个左边符不匹配。)]:Stack里为空。[():左边符还没有被正确关上。
Stack用Deque接口的LinkedList。不推荐用Stack。
代码
public class Solution {
private Map<Character,Character> parentheses = new HashMap<>();
{
parentheses.put('(',')');
parentheses.put('[',']');
parentheses.put('{','}');
}
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) { return false; }
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (parentheses.containsKey(chars[i])) {
stack.push(chars[i]);
continue;
}
if (parentheses.containsValue(chars[i])) {
Character top = stack.peek();
if (top == null) {
return false; //Exit2: Stack里没有内容!
} else {
if (parentheses.get(top) == chars[i]) {
stack.pop();
continue;
} else {
return false; //Exit1: 关闭符和上一个开始符匹配不上!
}
}
}
}
if (stack.size() == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false; //Exit3: Stack里还有开始符号没有被关闭!
}
}
}
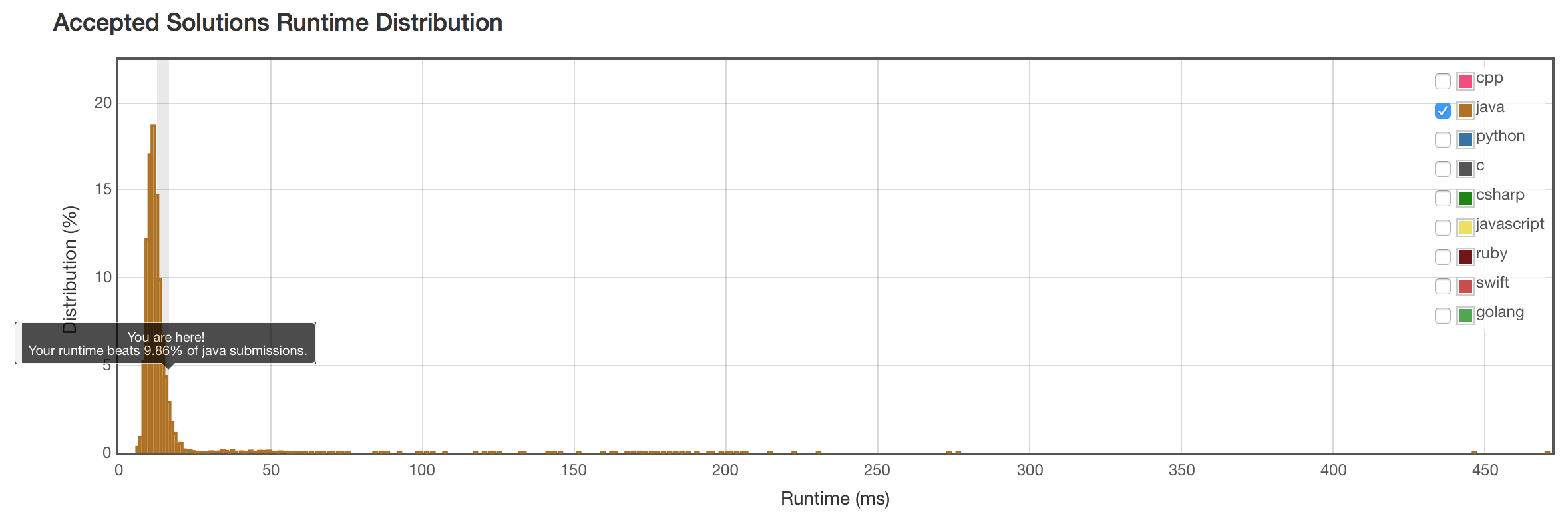
结果
代码简化
算法同上。代码整理地干净点。
代码
public class Solution {
private Map<Character,Character> parentheses = new HashMap<>();
{
parentheses.put('(',')'); parentheses.put('[',']'); parentheses.put('{','}');
}
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i); // next char
if (parentheses.containsKey(c)) {
stack.push(c);
continue;
}
Character top = stack.poll(); // Top char in Stack
if (top == null) { return false; }
if (parentheses.get(top) != c) { return false; }
}
return (stack.size() == 0)? true : false;
}
}
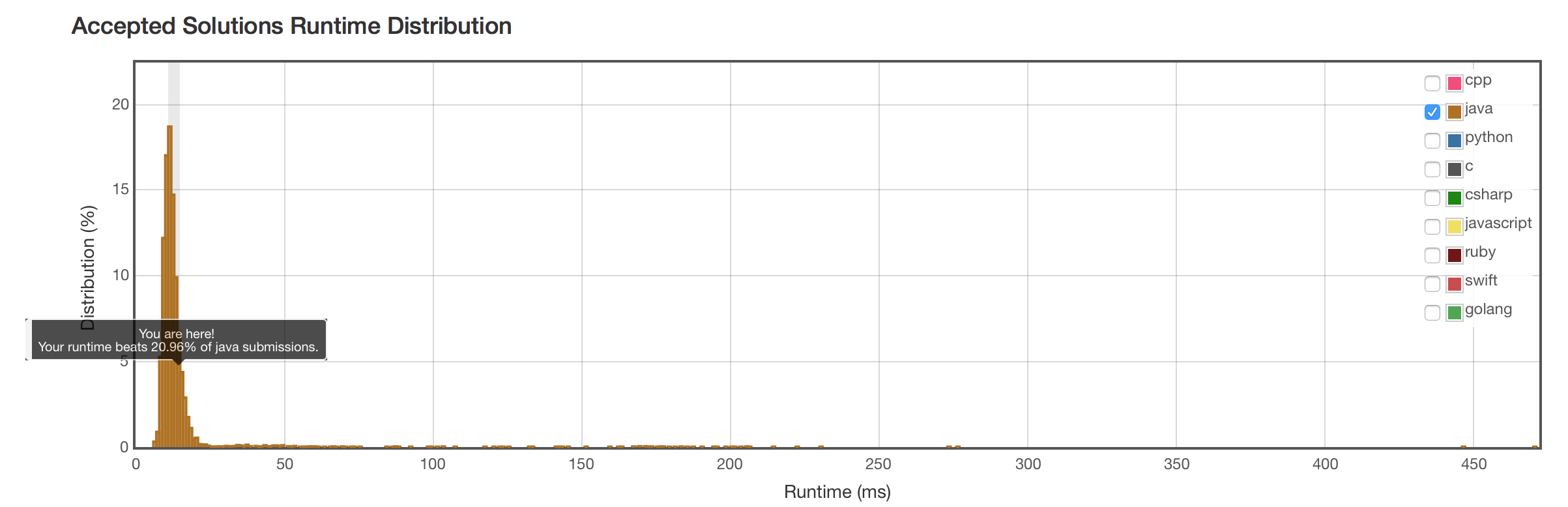
结果
继续简化
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '{' || c == '[' || c == '(') {
stack.push(c);
continue;
}
Character top = stack.poll();
if (top == null) { return false; }
if (c - top != 2 && c - top != 1) { return false; }
}
return (stack.size() == 0)? true : false;
}
}
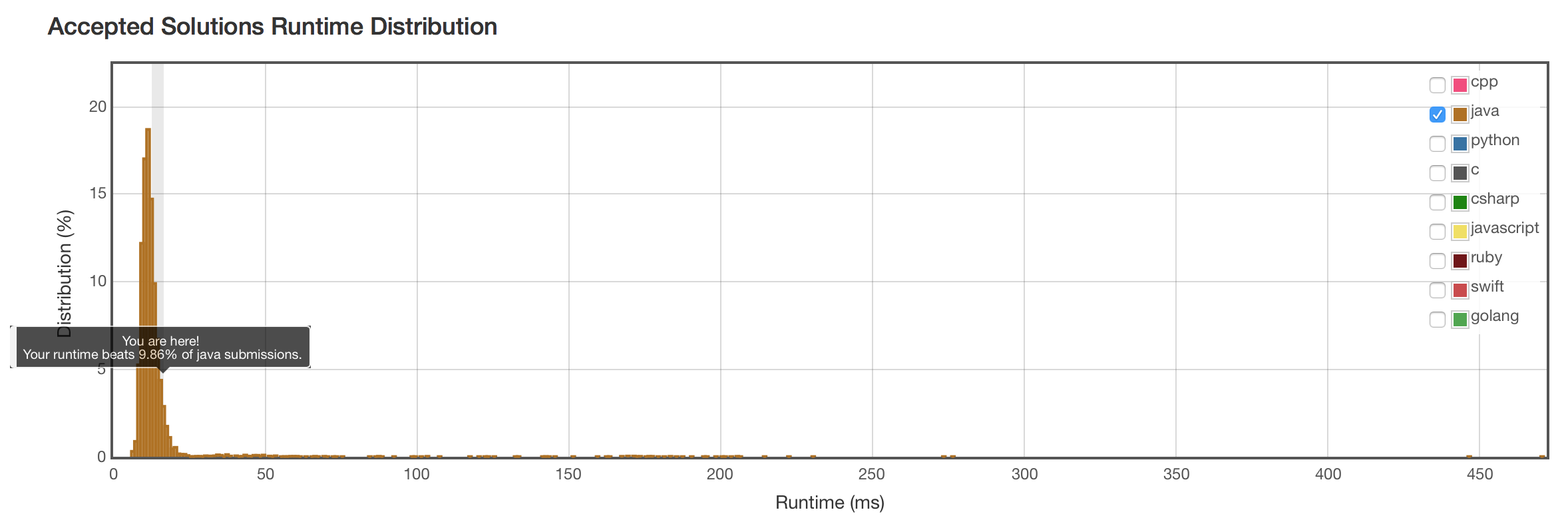
结果
继续简化
So sexy! I love my code!
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character> stack = new LinkedList<Character>();
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
if (c == '{') { stack.push('}'); continue; }
if (c == '[') { stack.push(']'); continue; }
if (c == '(') { stack.push(')'); continue; }
if (stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != c) { return false; }
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
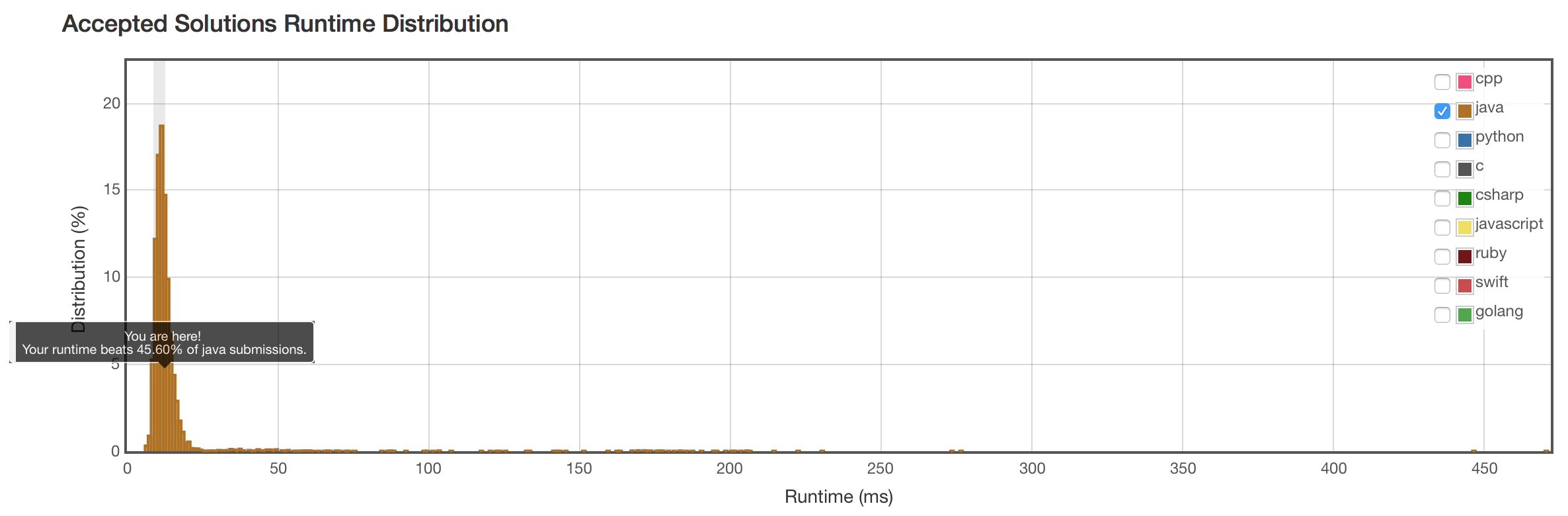
结果