题目
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
For example,
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
Your algorithm should use only constant space. You may not modify the values in the list, only nodes itself can be changed.
一次遍历 \(O(n)\)
一次遍历,使用一个ListNode temp的额外空间,用来暂存一个节点,然后交换节点。线性复杂度。
代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(0), cursor = sentinel;
sentinel.next = head;
while (cursor.next != null && cursor.next.next != null) {
ListNode temp = cursor.next;
cursor.next = cursor.next.next;
temp.next = cursor.next.next;
cursor.next.next = temp;
cursor = cursor.next.next;
System.out.println(sentinel.next);
}
return sentinel.next;
}
}
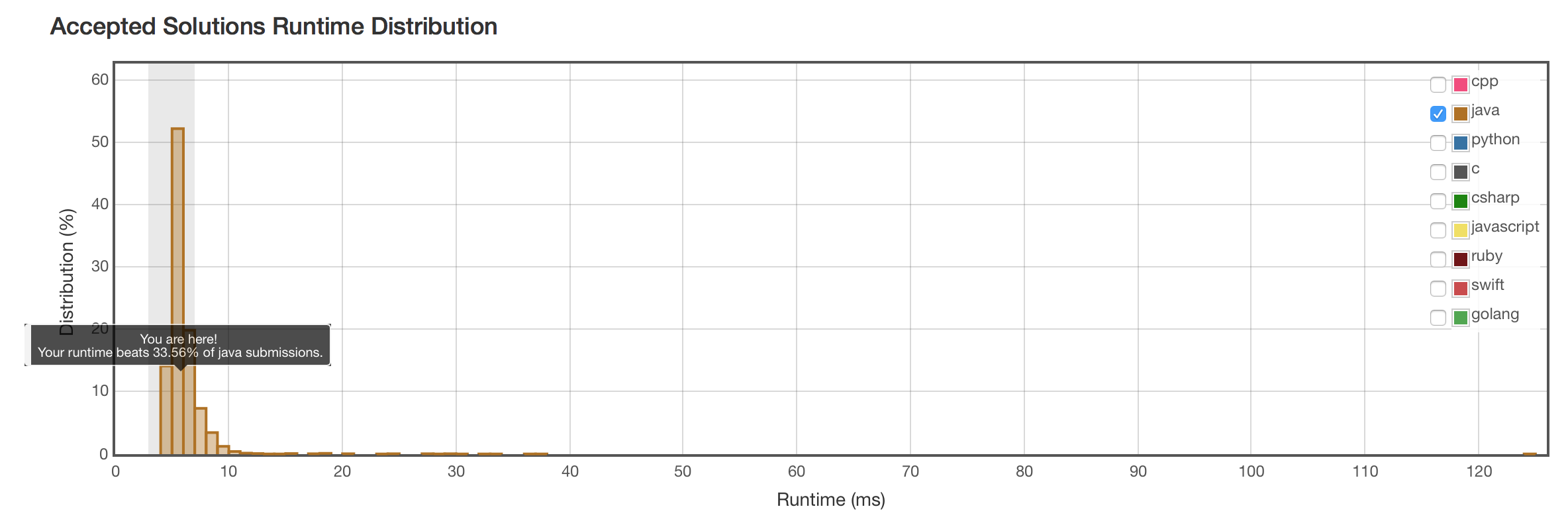
结果
不算好。还有银弹没找到。
还是一次遍历 \(O(n)\), 优化指针
与其用一个temp缓存空间,这次变成两个nextNode和afterNext。多一个缓存空间可以简化指针转换操作。但还是constant space,符合要求。
代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; }
ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(0);
sentinel.next = head;
ListNode cursor = sentinel, nextNode = cursor, afterNext = cursor;
while (cursor.next != null && cursor.next.next != null) {
nextNode = cursor.next;
afterNext = cursor.next.next;
nextNode.next = afterNext.next;
cursor.next = afterNext;
cursor.next.next = nextNode;
cursor = cursor.next.next;
}
return sentinel.next;
}
}
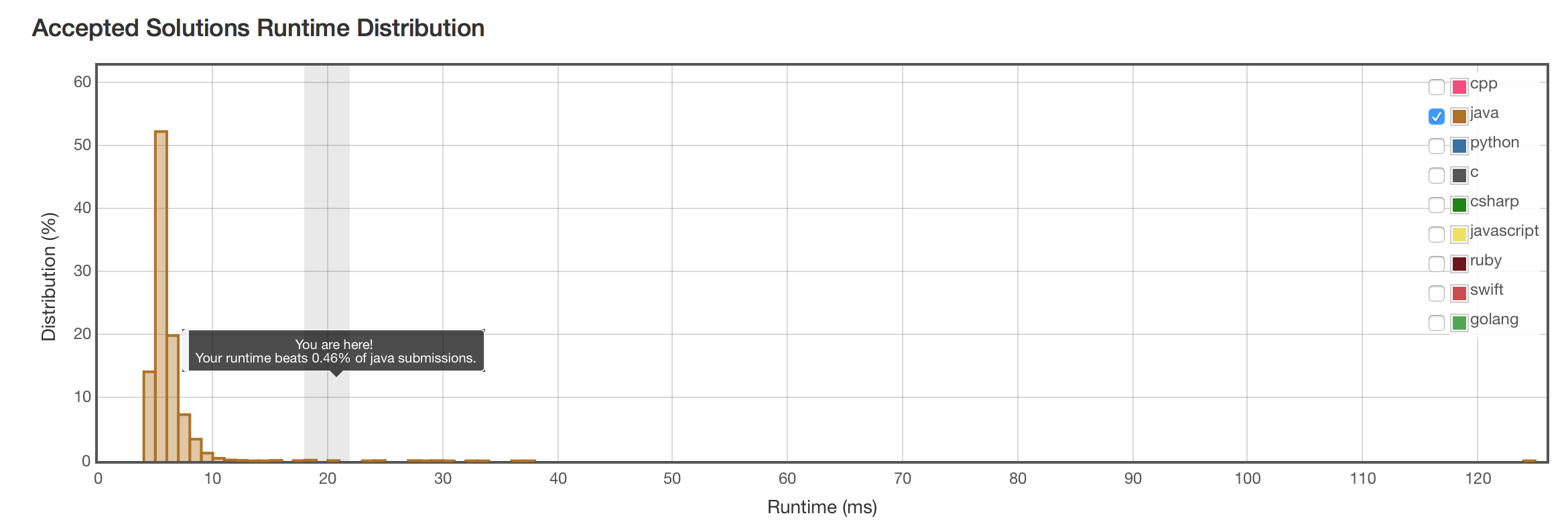
结果
这题不会有比\(O(n)\)好的银弹了。
递归版 \(O(n)\)
迭代版总能翻译成递归版。
代码
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; }
ListNode sentinel = new ListNode(0), cursor = sentinel;
sentinel.next = head;
ListNode nextNode = cursor.next, afterNext = nextNode.next;
swapPairsRecursive(cursor,nextNode,afterNext);
return sentinel.next;
}
public void swapPairsRecursive(ListNode cursor, ListNode nextNode, ListNode afterNext) {
nextNode.next = afterNext.next;
cursor.next = afterNext;
cursor.next.next = nextNode;
cursor = cursor.next.next;
if (cursor.next != null && cursor.next.next != null) {
swapPairsRecursive(cursor,cursor.next,cursor.next.next);
}
}
}
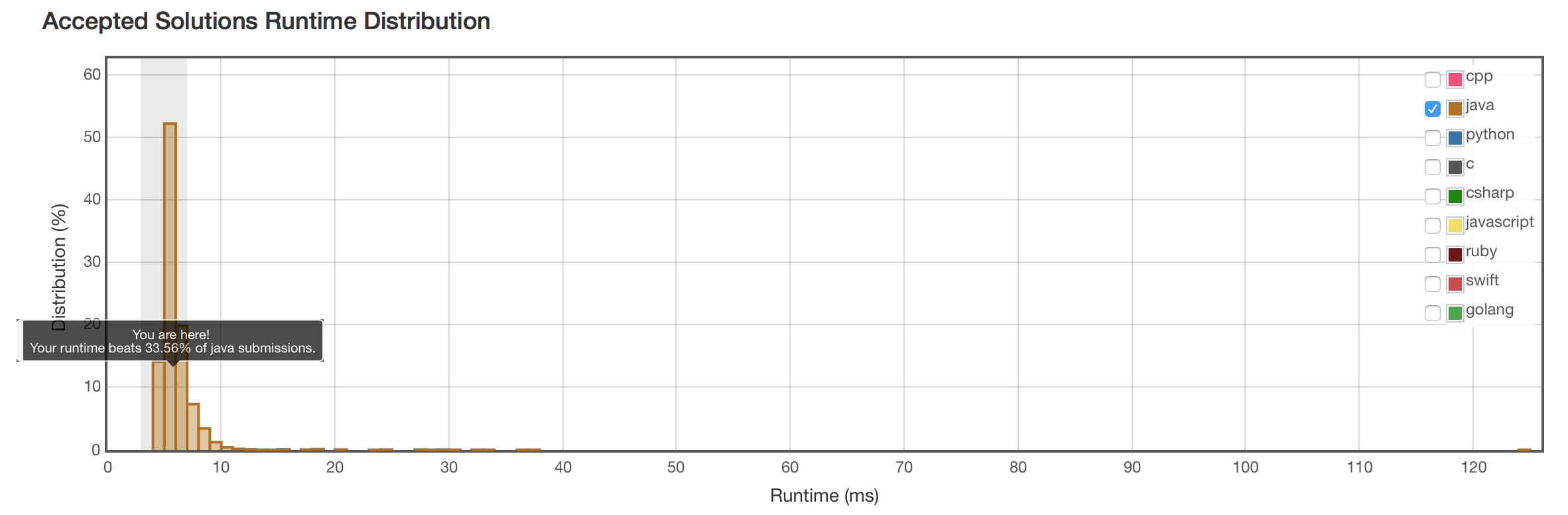
结果
结果是一样的。
简化版递归\(O(n)\)
不用把ListNode作为一个参数传递,直接作为返回值。递归能大幅简化。
代码
深度优先。非尾递归。
public class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) { return head; }
ListNode temp = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(temp.next);
temp.next = head;
return temp;
}
}
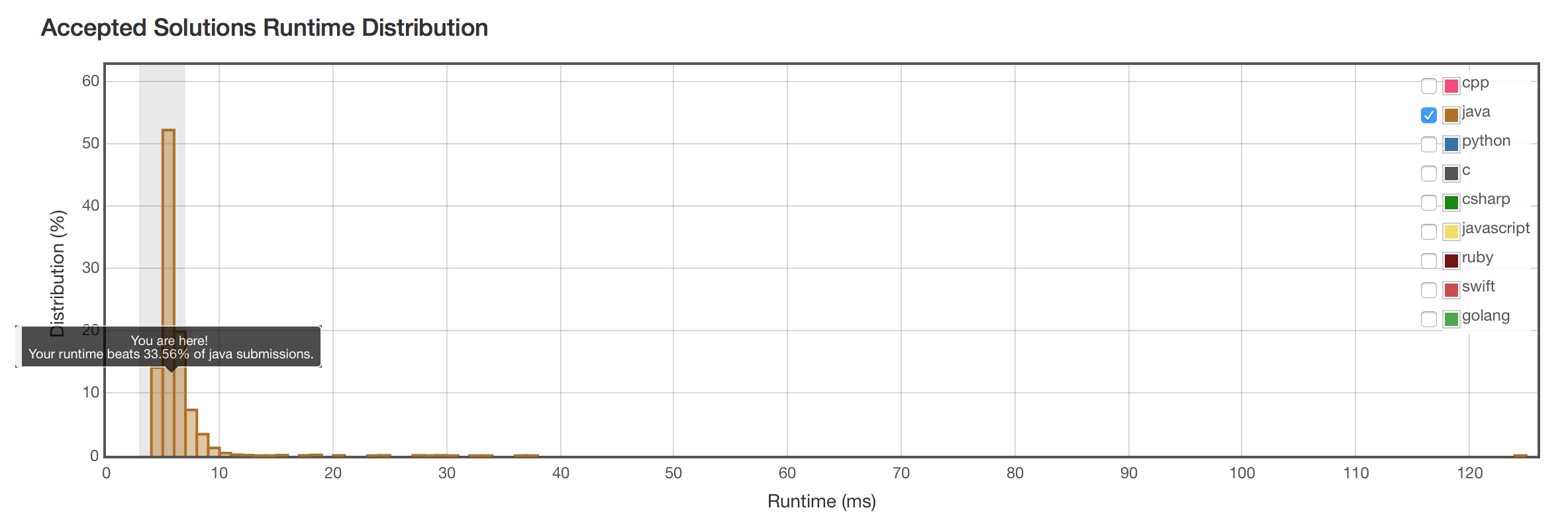
结果
结果不变。