题目
Implement strStr().
Returns the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or -1 if needle is not part of haystack.
正则表达式
偷懒的办法,直接正则表达式甩进去。
代码
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(needle);
Matcher m = p.matcher(haystack);
return (m.find())? m.start() : -1;
}
}
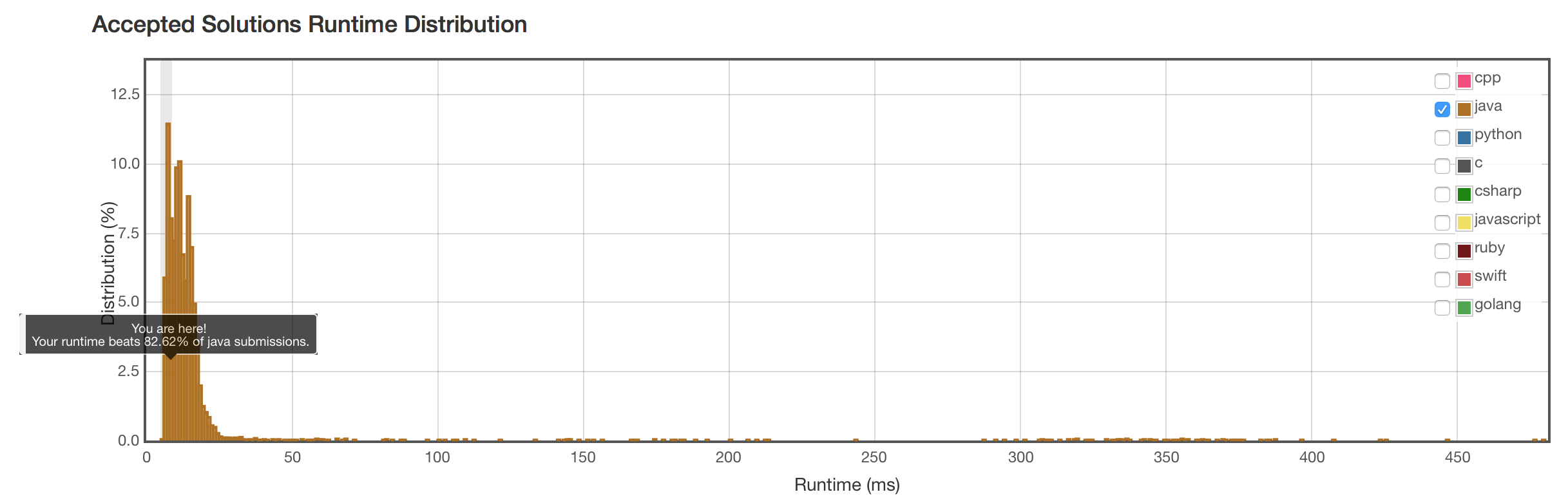
结果
看来正则表达式的效率比较捉急。
用String#equals()方法比较字符串
代码
public class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack.isEmpty() && needle.isEmpty()) { return 0; }
for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length() - needle.length() + 1; i++) {
if (haystack.substring(i,i+needle.length()).equals(needle)) { return i; }
}
return -1;
}
}
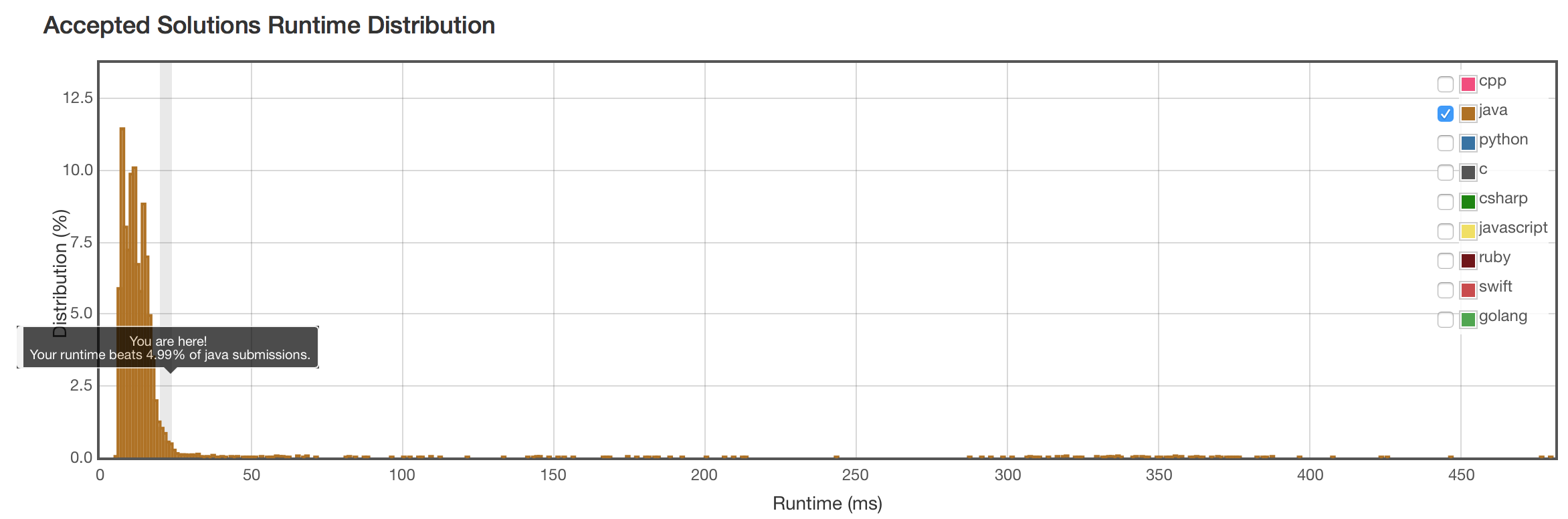
结果
不错。
手动逐个char地比较
代码
public class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
if (haystack.isEmpty() && needle.isEmpty()) { return 0; } // 唯一的特殊情况
char[] stackArray = haystack.toCharArray();
char[] needleArray = needle.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < stackArray.length - needleArray.length + 1; i++) {
int cursorNeedle = 0;
while (cursorNeedle < needleArray.length && stackArray[i+cursorNeedle] == needleArray[cursorNeedle]) {
cursorNeedle++;
}
if (cursorNeedle == needleArray.length) { return i; } // edge case needle.length() == 0 会从这里跳出。
}
return -1; // edge case haystack.length() == 0 不会进入for loop,直接到这里。
}
}
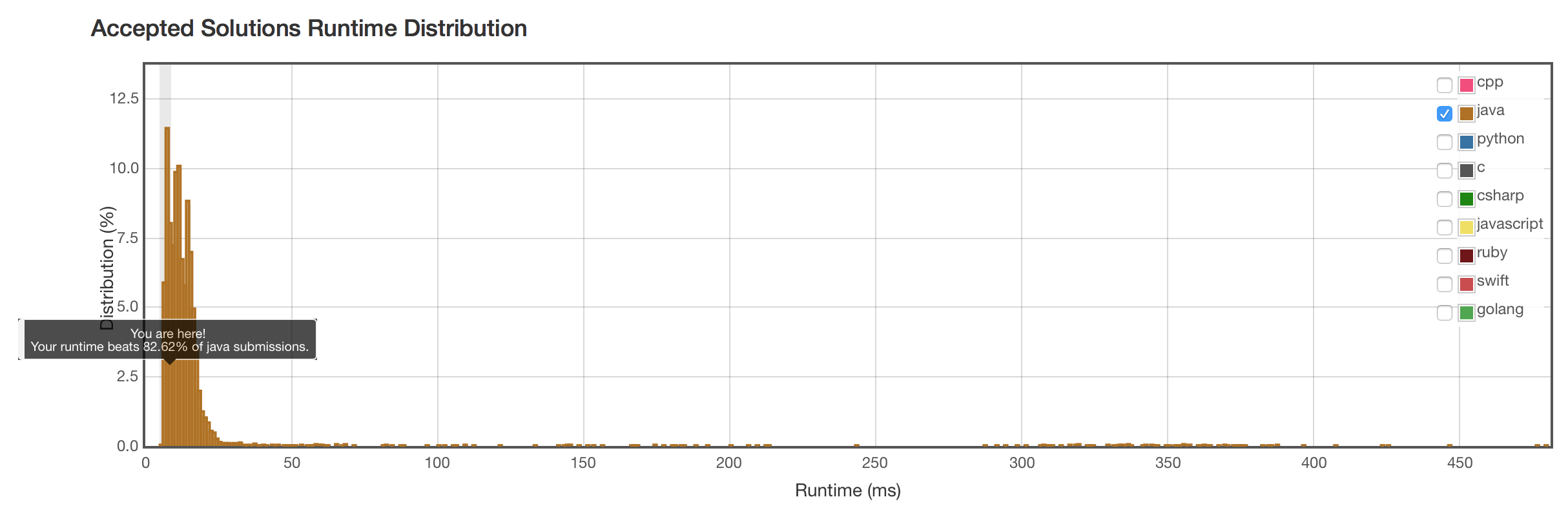
结果
和用String#equals()效率差不多。这说明,Java的String#equals()方法的复杂度还是线性的,没有什么黑魔法。