题目
Determine if a Sudoku is valid.
The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character ‘.’.
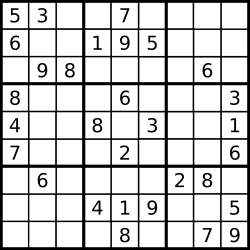
A partially filled sudoku which is valid.
Note: A valid Sudoku board (partially filled) is not necessarily solvable. Only the filled cells need to be validated.
The 3 Rules that a valid Sudoku must obey are:



按照3条规则,一条条来
先检查数组大小,是不是9x9见方。
再逐行检查,是不是每行都满足条件1.
再逐列检查,是不是每列都满足条件2.
再按照3x3小方格检查,是不是每个方格都满足条件3.
每次检查都事先准备一个{'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'}的ArrayList。contains()每找到一个数字就从列表里remove()。
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
if (board.length != 9 || board[0].length != 9) { return false; }
List<Character> nums = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(new Character[]{'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9'}));
if (! checkLine(board,nums)) { return false; }
if (! checkColumn(board,nums)) { return false; }
if (! checkSubBox(board,nums)) { return false; }
return true;
}
public boolean checkLine(char[][] board, List<Character> nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { // loop line
List<Character> copyNums = new ArrayList<>(nums);
for (int j= 0; j < board.length; j++) { // loop column
char num = board[i][j];
if (num != '.' && ! copyNums.contains(num)) {
return false;
} else if (num != '.') {
copyNums.remove(new Character(num));
}
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkColumn(char[][] board, List<Character> nums) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) { // loop column
List<Character> copyNums = new ArrayList<>(nums);
for (int i= 0; i < board.length; i++) { // loop line
char num = board[i][j];
if (num != '.' && ! copyNums.contains(num)) {
return false;
} else if (num != '.') {
copyNums.remove(new Character(num));
}
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkSubBox(char[][] board, List<Character> nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { // loop line
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { // loop column
List<Character> copyNums = new ArrayList<>(nums);
if (! checkThreeThreeBox(board,i*3,j*3,copyNums)) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkThreeThreeBox(char[][] board, int startHeight, int startWidth, List<Character> nums) {
for (int i = startHeight; i < startHeight+3; i++) { // loop line
for (int j = startWidth; j < startWidth+3; j++) { // loop column
char num = board[i][j];
if (num != '.' && ! nums.contains(num)) {
return false;
} else if (num != '.') {
nums.remove(new Character(num));
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
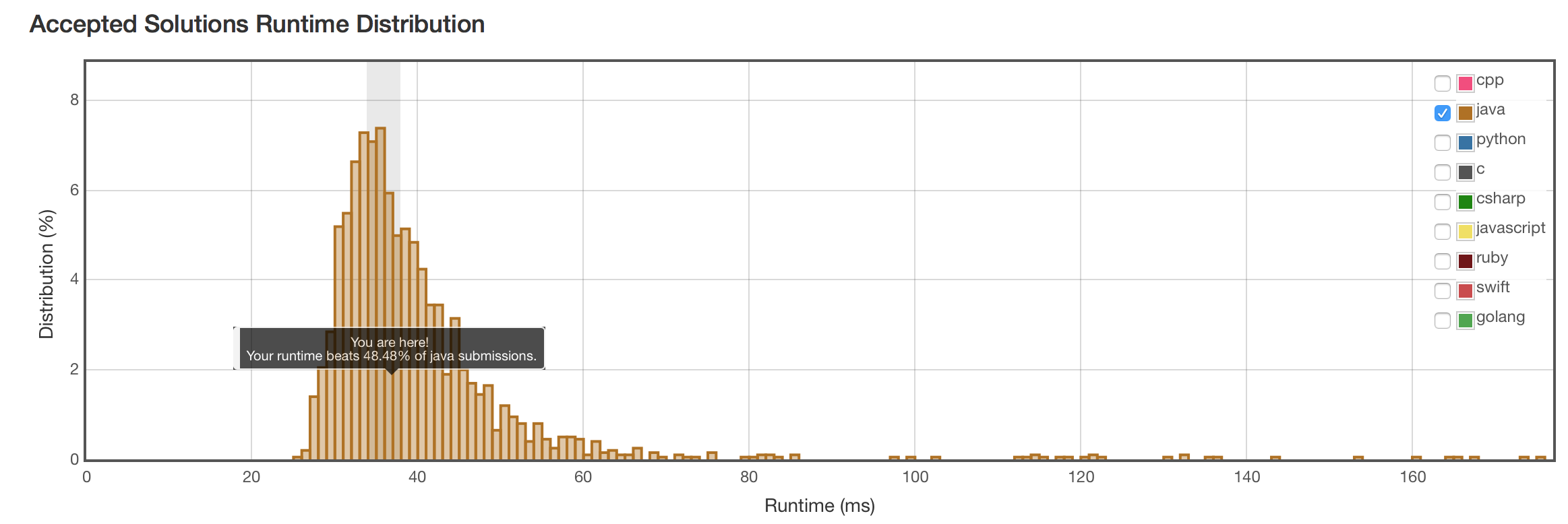
结果
还有提升空间。
考虑用BitMap来记录出现过的数字
用ArrayList太贵了。考虑用位操作的BitMap来记录数字出现历史信息。
用一个int的 低9位 做一个BitMap,分别代表1-9九个数字有没有出现过。
用1的左位移做掩码,比如,
...000000001 1 << 0
...000000010 1 << 1
...000000100 1 << 2
...000001000 1 << 3
...000010000 1 << 4
...000100000 1 << 5
...001000000 1 << 6
...010000000 1 << 7
...100000000 1 << 8
BitMap用0初始化。每来一个数字,用&操作判断之前是否出现过。
...000000000
...000000001 & 操作 // 检测1有没有出现过
---------------------------
...000000000 // 结果为0。说明1没有出现过。
如果一个数字没有出现过,就用|操作,在BigMap的对应位写上1。
...000000000
...000000001 | 操作
---------------------------
...000000001 // BitMap上现在记录了1已经出现过。
&操作需要同一位上都是1,才返回1。
0011 1100
0000 1101 & 操作 // 两个都是1,才是1.
-----------------------------
0000 1100
|操作只要同一位有一个是1,就返回1。
0011 1100
0000 1101 | 操作 // 有一个是1,就是1.
-----------------------------
0011 1101
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
if (board.length != 9 || board[0].length != 9) { return false; }
// assertion: size of array = 9 x 9
if (! checkLine(board)) { return false; }
if (! checkColumn(board)) { return false; }
if (! checkSubBox(board)) { return false; }
return true;
}
// if not duplicate number return the updated bitMap
// return MAX_VALUE if duplicate found
public int checkBitMap(int bitMap, char c) {
int num = c - '0';
if (num > 0 && num <= 9) { // 0-9的数字
int mask = 1 << (num-1);
if ( (bitMap & mask) == mask ) { // 数字重复
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
bitMap = bitMap | mask; // 数字没出现过,就把数字写进bitMap
}
} else {
if (c != '.') { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } //错误数字,既不是0-9,又不是‘.’
}
return bitMap;
}
public boolean checkLine(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) { // loop line
int bitMap = 0;
for (int j= 0; j < board.length; j++) { // loop column
bitMap = checkBitMap(bitMap,board[i][j]);
if (bitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkColumn(char[][] board) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) { // loop column
int bitMap = 0;
for (int i= 0; i < board.length; i++) { // loop line
bitMap = checkBitMap(bitMap,board[i][j]);
if (bitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkSubBox(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { // loop line
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { // loop column
if (! checkThreeThreeBox(board,i*3,j*3)) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
public boolean checkThreeThreeBox(char[][] board, int startHeight, int startWidth) {
int bitMap = 0;
for (int i = startHeight; i < startHeight+3; i++) { // loop line
for (int j = startWidth; j < startWidth+3; j++) { // loop column
bitMap = checkBitMap(bitMap,board[i][j]);
if (bitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
}
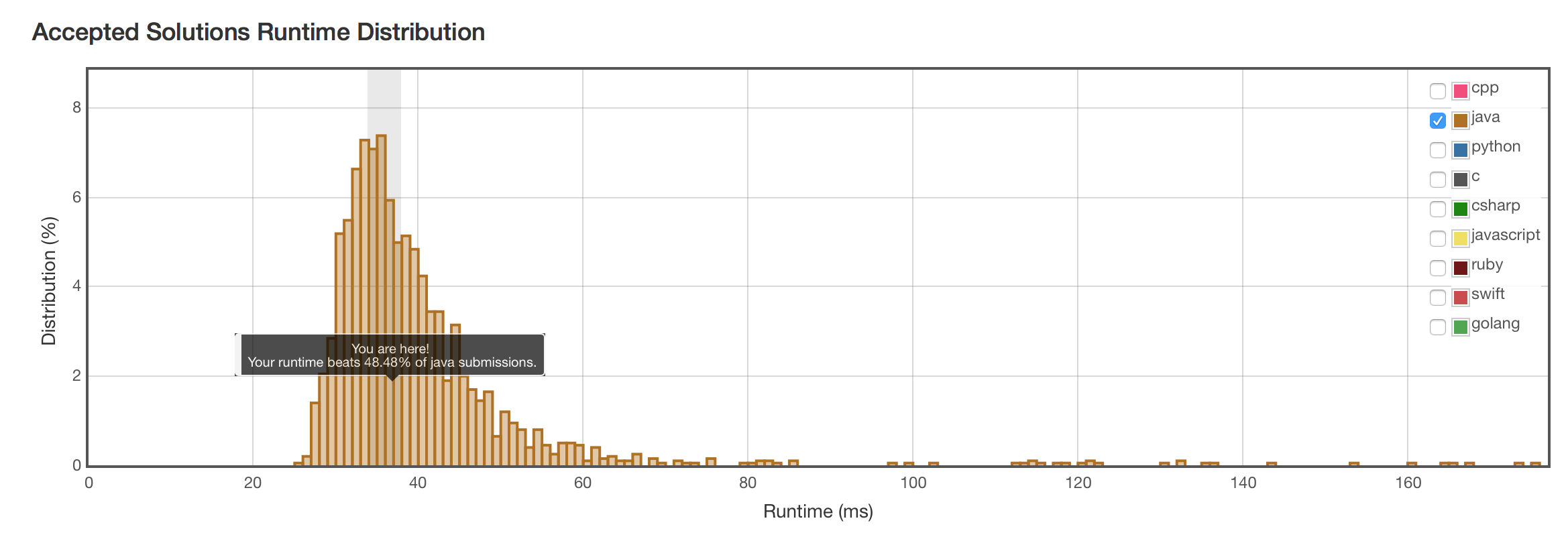
结果
快了一倍。
只遍历一次的解法
因为是9x9见方的数组,其实可以通过换算遍历指针,同时做行检验,列检验,和方块检验。
思路是,假设有i,j两个指针,分别遍历0-8。
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
// check line
// check column
// check box
}
}
行检验就是正常的board[i][j]。列检验取下标board[j][i]。方块检验需要换算一下。把9x9看成两层套嵌的3x3。第一层3x3的大box。每个大box打开,都有3x3的小box。i负责定位大box的index,j负责定位小box的index。
比如说,i=4,j=6的情况,
i = 4
4/3 = 1 //第2行的大box
4%3 = 1 //第2列的大box
--------------------------------
//所以是九宫格中间的那个3x3大box
j = 6
6/3 = 2 //第3行的小box
6%3 = 0 //第1列的小box
--------------------------------
//所以是中心3x3大box里的:第3行,第1列那个小box
取得的小box的坐标具体为:board[boxLineIndex*3+j/3][boxColumnIndex*3+j%3]。
代码
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
if (board.length != 9 || board[0].length != 9) { return false; }
// assertion: size of array = 9 x 9
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
int lineBitMap = 0;
int columnBitMap = 0;
int boxBitMap = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < board.length; j++) {
// check for line
lineBitMap = checkBitMap(lineBitMap,board[i][j]);
if (lineBitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
// check for column
columnBitMap = checkBitMap(columnBitMap,board[j][i]);
if (columnBitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
// check for each box
int boxLineIndex = i/3;
int boxColumnIndex = i%3;
boxBitMap = checkBitMap(boxBitMap,board[boxLineIndex*3+j/3][boxColumnIndex*3+j%3]);
if (boxBitMap == Integer.MAX_VALUE) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
/**
* if not duplicate number return the updated bitMap
* return MAX_VALUE if duplicate found
*/
public int checkBitMap(int bitMap, char c) {
int num = c - '0';
if (num > 0 && num <= 9) { // number 0-9
int mask = 1 << (num-1);
if ( (bitMap & mask) == mask ) { // duplicate number
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
} else {
bitMap = bitMap | mask; // first occurrence
}
} else {
if (c != '.') { return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } // wrong char, neither 0-9, nor "."
}
return bitMap;
}
}
不用BitMap,换成现成的HashSet,代码更简洁
public class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
for(int i = 0; i<9; i++){
HashSet<Character> rows = new HashSet<Character>();
HashSet<Character> columns = new HashSet<Character>();
HashSet<Character> cube = new HashSet<Character>();
for (int j = 0; j < 9;j++){
if(board[i][j]!='.' && !rows.add(board[i][j])) { return false; }
if(board[j][i]!='.' && !columns.add(board[j][i])){ return false; }
int RowIndex = 3*(i/3);
int ColIndex = 3*(i%3);
if(board[RowIndex + j/3][ColIndex + j%3]!='.' && !cube.add(board[RowIndex + j/3][ColIndex + j%3])) { return false; }
}
}
return true;
}
}
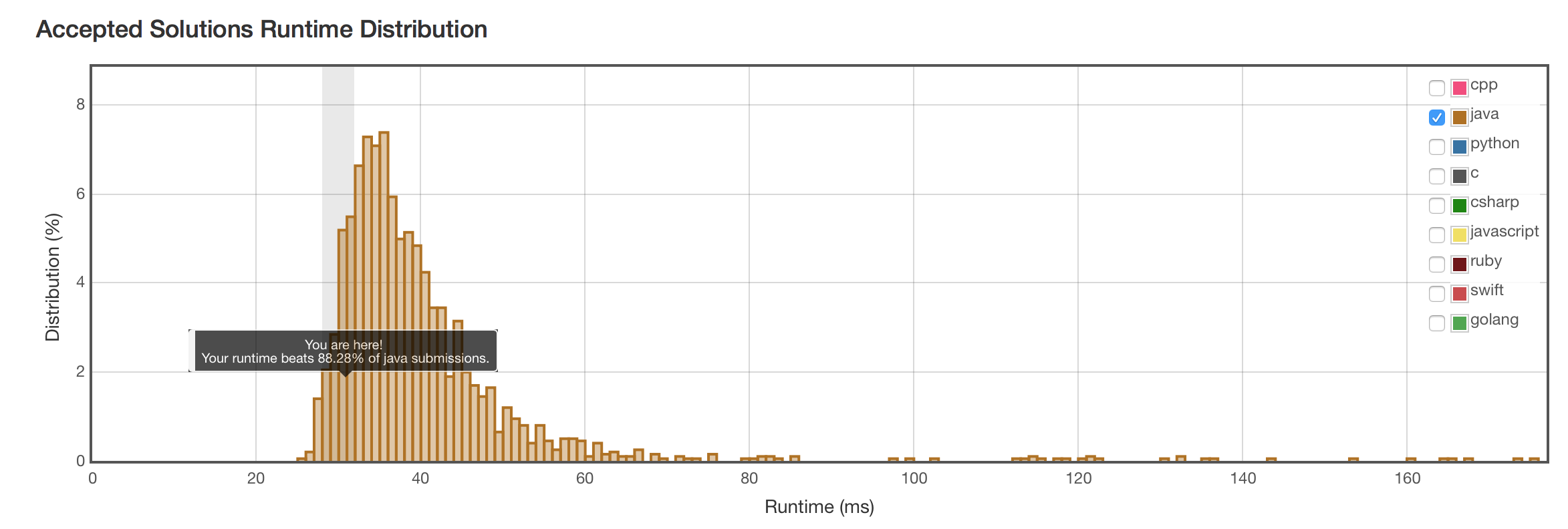
结果