File
File的本质是一个“文件地址标识”。内部维护着表示绝对路径的String。
private String path;
File不是单指某一个文件,而是 “绝对地址” 目录下的所有文件。“注意”:不迭代目录。只返回第一层的文件列表。
- File对象比单纯文件名更有用。因为包含了更多有用的信息。
File#list()
“绝对地址” 目录下的所有文件列表可以用 File#list() 方法得到。
public String[] list() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(path);
}
return fs.list(this);
}
这个方法调用的fs:指的是native数据FileSystem。所以返回文件列表的动作是系统替我们完成的。不是用Java实现的。
static private FileSystem fs = FileSystem.getFileSystem();
但我们还是可以对返回的List有所控制。通过给list()方法传入一个FilenameFilter对象做参数。
public String[] list(FilenameFilter filter) {
String names[] = list();
if ((names == null) || (filter == null)) {
return names;
}
List<String> v = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0 ; i < names.length ; i++) {
if (filter.accept(this, names[i])) {
v.add(names[i]);
}
}
return v.toArray(new String[v.size()]);
}
list()方法会回调FilenameFilter对象的accept()方法,判断某个文件是否符合过滤条件。accept()方法用个正则表达式就行了。
File path = new File(".");
String[] list = path.list(new FilenameFilter() {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(args[0]);
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return pattern.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
这是一个标准的“策略模式”的良好实践。
递归获取某个地址下的所有文件
非常常用的功能。完全可以写进自己的类库。
具体实现参见本章练习4,5,6.
“流(Stream)”家族
Java IO有60个类。但只要思路清晰,它们各自的用途还是很明确的。
两大家族:面向字节 & 面向字符
首先要明确,IO有两大家族:
- InputStream, OutputStream:面向字节。
- Reader, Writer:面向字符。
上两张全家福:
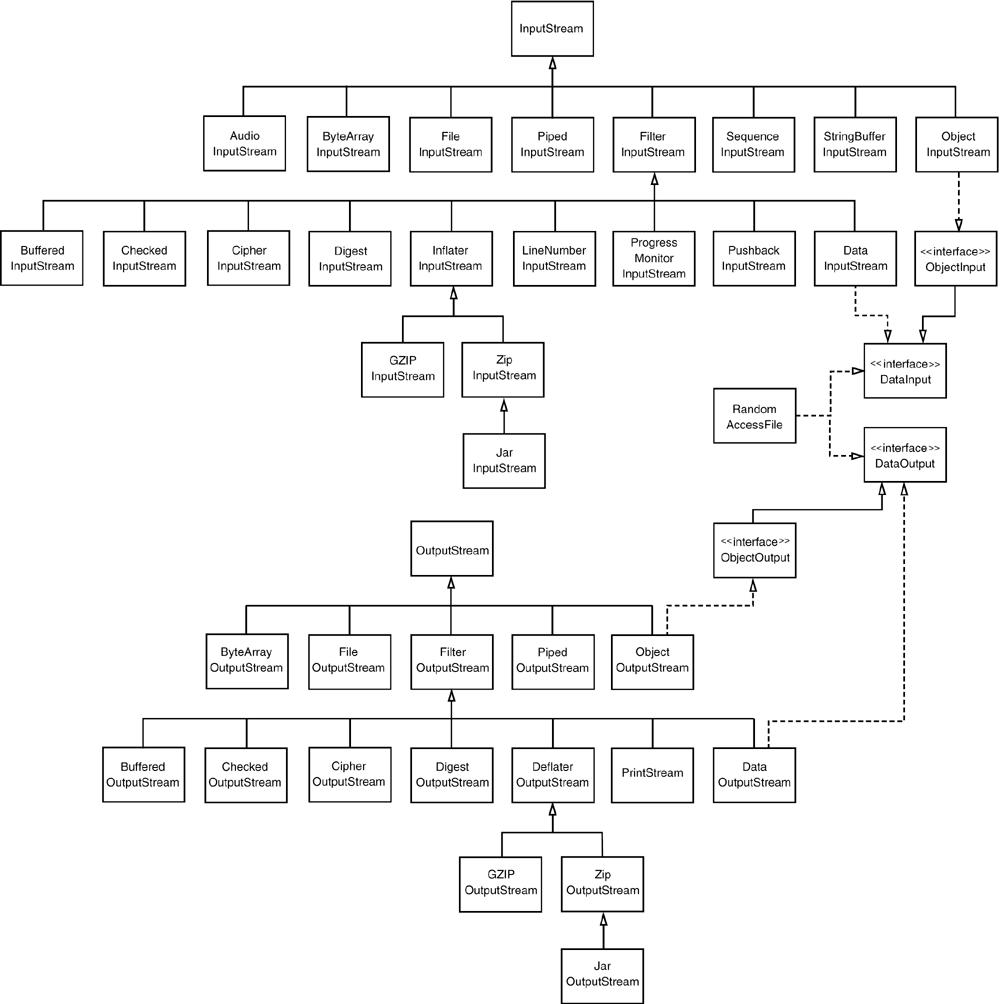
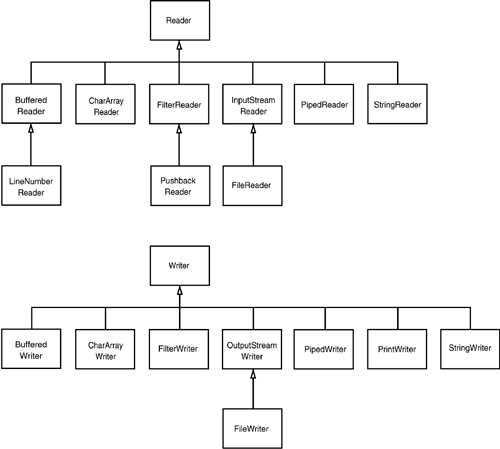
字节到字符的编码
什么是面向字节?什么是面向字符?先要从最基本的概念说起:
- 一个字节(byte):8 bit
- 一个字符(char):16 bit Unicode
基本单位一个”字节“占8个bit。这很简单。Java里的基本字符char基于UTF-16。和只占一个字节的ASCII码不同,常规字符占用两个字节,16 bit。
要搞懂各种编码之间的前世今生,推荐下面这篇比较好懂的文章: 《字符编码笔记:ASCII,Unicode和UTF-8》
ASCII
简单讲就是,一个字节8 bit,最多为256个符号编码。所以英语26个字母,再加几个常用符号,标点,256个码位足够了。这就熟悉的ASCII码。如下图,ASCII码一共收录了空格及94个“可印刷字符”。
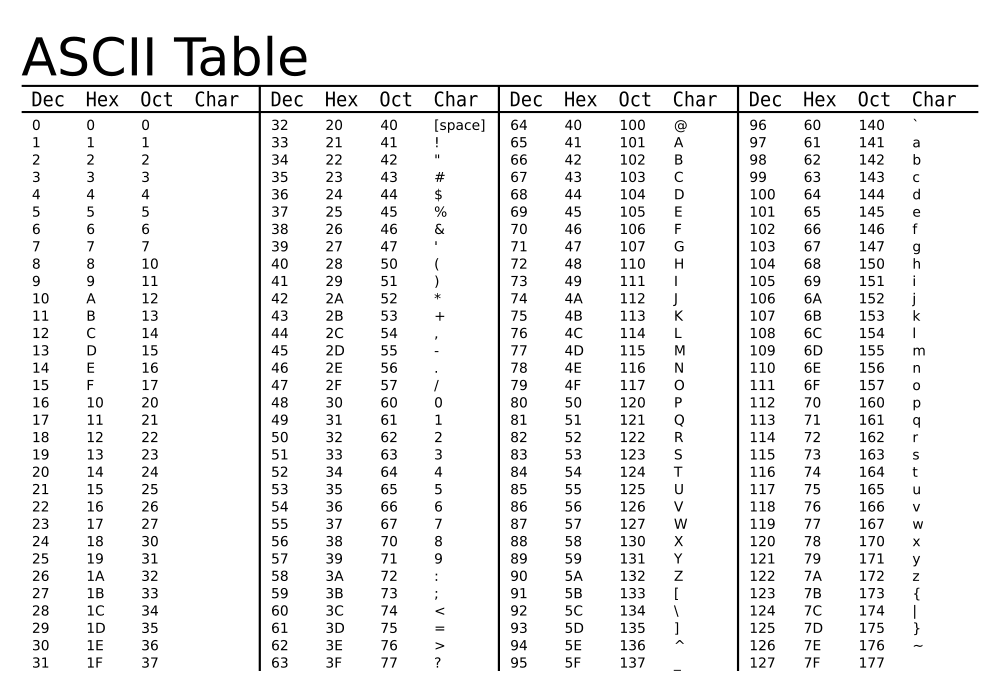
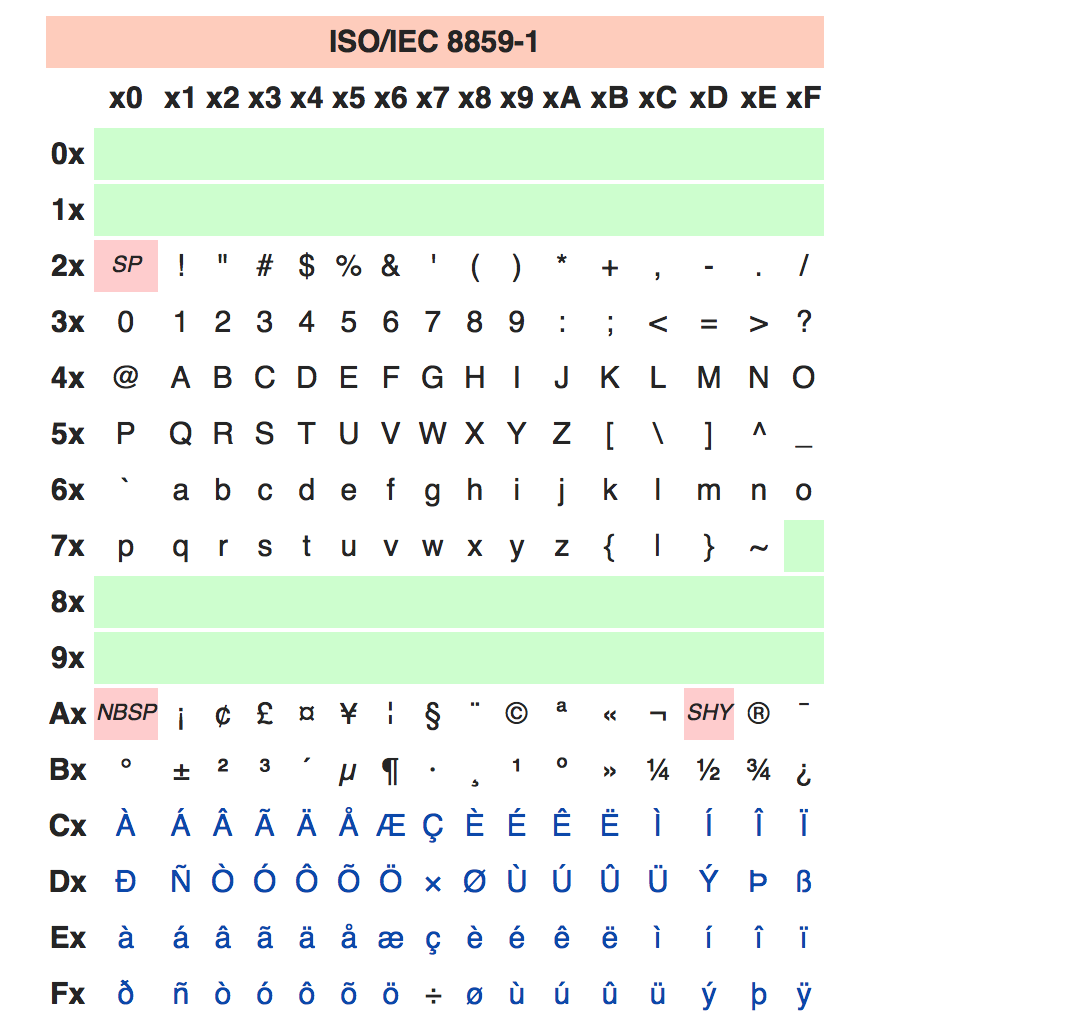
ISO/IEC 8859-1
ASCII给英语用足够了。但其他的语言,比如拉丁语系的法语西班牙语等语言都有自己的特殊字母。所以,世界的每个不同地区又有了自己的特殊编码标准。比如ISO/IEC 8859-n系就是国际标准化组织定义的一系列8位字符集。也只占一个字节。最常用的比如ISO/IEC 8859-1就是法语,芬兰语所用的西欧字符集。
中文编码
汉字有好几万个。编码一个8 bit,256个码位就不够了。所以我国的汉字编码现行标准是《GB 18030》。每个字可以由1个、2个或4个字节组成,编码空间有161万个字符。另一个中国常用编码集是Big5。全世界各国都有自己的《字元编码标准》。
Unicode
但这样编码的缺点很明显,同一个文件,到了另一个国家,用另一套编码集来解码,会产生乱码。在全球化的今天,最好全世界有一套统一的字符编码集。这就是《Unicode》。Unicode的理念就是那么直接 – 每种不同语言的不同字符都有一个单独编码。最初,Unicode占用2个字节,最多编码256*256=65536个字符。但很快从3.1版本开始就不够用了。所以又搞出了附加字符集。附加字符用4个字节表示。目前Unicode已对总共超过12万个字符编码。
UTF-8
这里需要搞清楚一件事:Unicode只是一套符号的编码。但计算机具体怎么读取这套编码,又是另外一件事。
我们可以老老实实地用2个字节,16位来表示一个Unicode字符。每次老老实实读取两个字节。然后在读到某个特殊标记的时候,知道是附加字符集,需要再往后读2个字节。但由于英语是使用最广泛的语言,明明一个字符就能完成,现在非要用2个字符。浪费了内存空间。不符合编码的规范:常用字符用最短的编码。所以就要想办法怎么能用一个字节表示英语,其他字符用多个字节。而且又要让电脑能够识别,自动处理。这就是UTF-8做的事。一本正经下定义的话:关键就是可变长编码。
- UTF-8(8-bit Unicode Transformation Format)是一种针对Unicode的可变长度字元编码,也是一种前缀码。
UTF-8编码规则,如下图。可变长编码的关键就是:怎么让电脑知道每次需要读多大长度。所以必然需要某种标识。
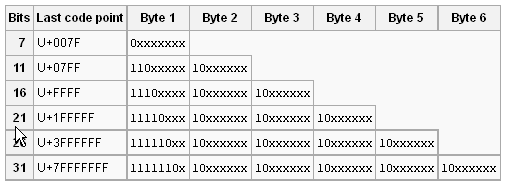 具体的规则,很简单,只有两条:
具体的规则,很简单,只有两条:
- 对于单字节的符号,字节的第一位设为0,后面7位为这个符号的unicode码。因此对于英语字母,UTF-8编码和ASCII码是相同的。
- 对于n字节的符号(n>1),第一个字节的前n位都设为1,第n+1位设为0,后面字节的前两位一律设为10。剩下的没有提及的二进制位,全部为这个符号的unicode码。
UTF-16
UTF-16和UTF-8的不同在于,它用2个字节表示一些常用字符,4个字节表示附加字符。
具体编码规则,参见《使用 Java 语言进行 Unicode 代理编程》这篇文章。
优先考虑面向字符的流
如果使用面向字节的流,那我们就必须自己处理上面介绍的从字节到字符的编码转换工作。比如根据UTF-16编码规则把byte[]数组解码成String字符串。虽然String类的构造器可以完成编码到字符映射的工作,一个String对象也有getBytes()方法反向编码。
String s = "我是沈玮";
byte[] b = s.getBytes("UTF-8");
String n = new String(b,"UTF-8");
但这样也增加了很多工作量。所以大多数情况应该优先使用面向字符的流。
关于Java的编码问题,也有一篇好的阅读材料:《深入分析 Java 中的中文编码问题》。
数据的编码
除了byte到char需要编码和解码,其他基本型也不是直接读取就可以的。不同数据类型有不同的长度,而且内部数据编排原理也各不相同。以双精度浮点数double为例,
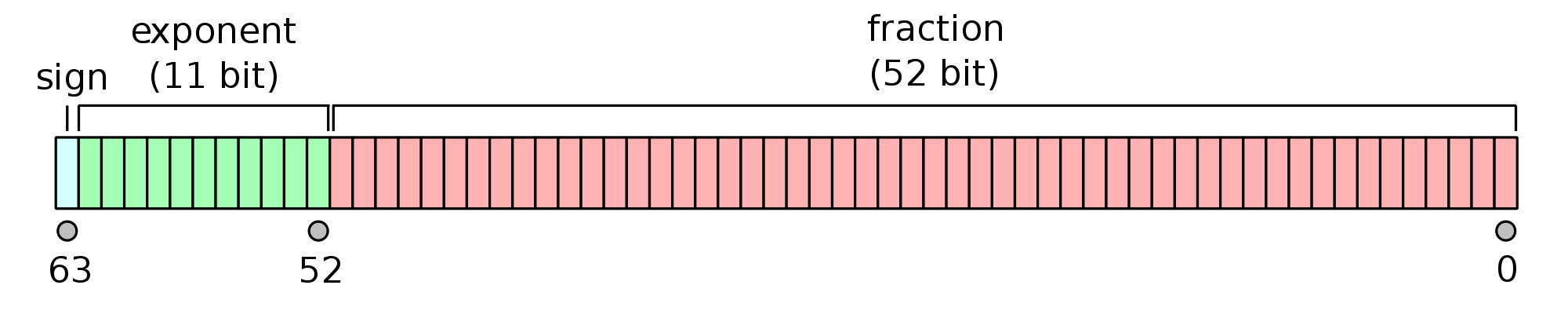 首先,double型的长度为64 bit。占据8个字节。最高位63位表示正负号,62-52的高11位为指数位,51-0的低52位表示尾数。
首先,double型的长度为64 bit。占据8个字节。最高位63位表示正负号,62-52的高11位为指数位,51-0的低52位表示尾数。
对double型的解码,虽然不需要一个几十万规模的字符集,但也需要一个转换。
装饰器模式
装饰器模式的基本思想很简单,就是利用组合和代理为类添加新功能。
比如一个最简单的容器模型Basic类。
class Basic {
private String value;
public void set(String val) { value = val; }
public String get() { return value; }
}
需要有一个所有装饰器的基类。把Basic类作为一个成员字段,以及一个以Basic类对象为参数的构造器。其实就是简单地用一个Basic对象做代理,封装所有方法。
class Decorator extends Basic {
protected Basic basic;
public Decorator(Basic basic) { this.basic = basic; }
public void set(String val) { basic.set(val); }
public String get() { return basic.get(); }
}
所有的装饰类继承原始装饰器基类后,可以在原有Basic基础上添加新功能。而它的构造器就是一个普通Basic类。
class TimeStamped extends Decorator {
private final long timeStamp;
public TimeStamped(Basic basic) {
super(basic);
timeStamp = new Date().getTime();
}
public long getStamp() { return timeStamp; }
}
Java IO为什么用装饰器模式?
Java用装饰器模式实现IO,主要是为了减少库中类的数量。通过拼装有限的功能组件,最终实现具有复合型功能的IO工具。
虽然Java IO包里类一点也不少,一共有60个类。但它们能够组合出来的具有不同功能的工具数量更是惊人。这么说,Java IO虽然有点难用,但还是挺成功的。
谁直接接触数据源?谁用来装饰?
要理清IO包的脉络,一定要明确一个思路,IO包中的类分为两种不同的角色:
- 一类是直接对数据源进行读写的。
- 另一类是添加功能的过滤器。
“核心IO”:负责直接读写特定类型数据源。以(InputStream,OutputStream),或者(Reader,Writer)为基类。 * File######: * String######: * ByteArray######(or: CharArray######): * Piped######: * Zip######:
“过滤器”:负责改变流的行为。以(FilterInputStream,FilterOutputStream),或者(FilterReader,FilterWriter)为基类。 * Buffered######: * Data######: * Print######: * Pushback######:
组合流过滤器
一般使用IO包的模式就是:在核心IO类的外面套过滤器。
考虑下面这个例子:
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File(Data.txt))));
FileInputStream负责从本地文件读取字节流。然后套上一层BufferedInputStream缓冲器,避免频繁读取磁盘。最后还要套上DataInputStream装饰器,为的是方便读取不同类型的数据。
构造器层面,能够这样装配,因为FileInputStream有一个接受File为参数的构造器。BufferedInputStream和DataInputStream都有一个接受InputStream为参数的构造器。这就是装饰器模式的工作方式。
我们把DataInputStream套在最外面,最后暴露给我们的是DataInputStream类的接口,这是因为我们要用的就是DataInputStream所独有的比如readInt(), readDouble()这样方便读取数据的方法。
我们把BufferedInputReader夹在中间,但不用担心他的功能被覆盖掉。因为DataInputStream读取数据的方法,比如readInt()最终调用的都是read()方法(源代码如下):
public final int readInt() throws IOException {
int ch1 = in.read();
int ch2 = in.read();
int ch3 = in.read();
int ch4 = in.read();
if ((ch1 | ch2 | ch3 | ch4) < 0)
throw new EOFException();
return ((ch1 << 24) + (ch2 << 16) + (ch3 << 8) + (ch4 << 0));
}
因为int型占4个字节,所以调用4次read()方法。由于DataInputStream没有定义自己的无参数read()方法。所以根据其基类FilterInputStream类的无参数read()方法,直接调用的就是BufferedInputStream的read()方法。
public int read() throws IOException {
return in.read();
}
而BufferedInputStream的read()方法是实现了缓冲功能的。所以BufferedInputStream的缓冲作用也得以发挥。同时又拥有了DataInputStream的特殊数据读取接口。
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) {
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
所以一般把DataInputStream或者PrintStream这种拥有特殊接口的类套在最外面,然后把BufferedInputStream夹在中间,最后由FileInputStream或者StringInputStream负责直接面对数据源,是套嵌多层过滤器的通用做法。
缓冲器Buffer是怎么工作的?
作为最常用的过滤器,每个流不管是输入还是输出都会被套上一层“缓冲器”。缓冲器的原理其实很简单:一次性读取很多数据到内存,作为缓存,以后每次read就从缓存里取,而不是每次都磁盘操作读取实际文件。输出缓冲的原理也是一样,多攒一点内容才执行实际读写。下面代码是BufferedInputStream的部分源码:
public class BufferedInputStream extends FilterInputStream {
private static int defaultBufferSize = 8192;
/**
* The internal buffer array where the data is stored. When necessary,
* it may be replaced by another array of
* a different size.
*/
protected volatile byte buf[];
//... ...
}
可以看到,BufferedInputStream的缓冲区是一个字节数组byte buf[]。默认大小是8192字节,总共64k bit。
下面是它的read()方法。很简单,如果缓存读完了,就执行fill()方法重新填充。否则就直接用getBufIfOpen()方法读取缓存数组。其中pos作为数组的游标。
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (pos >= count) { //缓存读完
fill();
if (pos >= count)
return -1;
}
return getBufIfOpen()[pos++] & 0xff;
}
getBufIfOpen()方法就是简单返回缓存数组。
/**
* Check to make sure that buffer has not been nulled out due to
* close; if not return it;
*/
private byte[] getBufIfOpen() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = buf;
if (buffer == null)
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
return buffer;
}
fill()方法稍微复杂一点,但抛开前面的各种安全检测,最后就是用getInIfOpen()方法获取它装饰的输入流。然后调用被装饰输入流的read()方法读取数据,放到缓存buffer里。
/**
* Fills the buffer with more data, taking into account
* shuffling and other tricks for dealing with marks.
* Assumes that it is being called by a synchronized method.
* This method also assumes that all data has already been read in,
* hence pos > count.
*/
private void fill() throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = getBufIfOpen();
if (markpos < 0)
pos = 0; /* no mark: throw away the buffer */
else if (pos >= buffer.length) /* no room left in buffer */
if (markpos > 0) { /* can throw away early part of the buffer */
int sz = pos - markpos;
System.arraycopy(buffer, markpos, buffer, 0, sz);
pos = sz;
markpos = 0;
} else if (buffer.length >= marklimit) {
markpos = -1; /* buffer got too big, invalidate mark */
pos = 0; /* drop buffer contents */
} else { /* grow buffer */
int nsz = pos * 2;
if (nsz > marklimit)
nsz = marklimit;
byte nbuf[] = new byte[nsz];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, nbuf, 0, pos);
if (!bufUpdater.compareAndSet(this, buffer, nbuf)) {
// Can't replace buf if there was an async close.
// Note: This would need to be changed if fill()
// is ever made accessible to multiple threads.
// But for now, the only way CAS can fail is via close.
// assert buf == null;
throw new IOException("Stream closed");
}
buffer = nbuf;
}
count = pos;
int n = getInIfOpen().read(buffer, pos, buffer.length - pos);
if (n > 0)
count = n + pos;
}
一些常见使用场景
把握住上面这个组合装饰器的原则,java IO的一些习惯用法就很好理解了。
读取本地文本文件
一般Unicode编码的文本文件,可以用面向字符的FileReader读取,再套一个缓冲器BufferedReader。
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(Data.txt)));
从内存读取
一般把数据封装成String,然后用StringReader读取。
String s = "Hello World!";
StringReader br = new StringReader(s);
格式化内存读取
格式化读取就必须用DataInputStream。因为DataInputStream是面向字节的,可以用把String打散成byte[]数组,然后用ByteArrayInputStream读取。
String s = "Hello World!";
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(s.getBytes()));
基本文件输出
写入本地文件,最好用PrintWriter。
PrintWriter pr = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File(Data.txt))));
文件输出快捷方式
PrintWriter有一个直接接受File为参数的构造器。
PrintWriter pr = new PrintWriter(new File(Data.txt));
底层“输入”“输出”是怎么实现的?
到目前为止,所有的描述到了附着于具体数据读写对象的“核心IO”类就结束了。具体的读写操作被想象成一个“黑箱”过程。这里,以FileInputStream为例,解释一下,一个本地文件到底是怎么被打开,然后读取到内存的。此处主要参考了[** 《JNI探秘—–你不知道的FileInputStream的秘密》 ](http://www.cnblogs.com/zuoxiaolong/p/jni1.html)这篇文章。感谢作者 – **左潇龙。
先看FileInputStream源码中的一小段:
public class FileInputStream extends InputStream {
/* File Descriptor - handle to the open file */
private FileDescriptor fd;
private FileChannel channel = null;
public FileInputStream(String name) throws FileNotFoundException {
this(name != null ? new File(name) : null);
}
public FileInputStream(File file) throws FileNotFoundException {
String name = (file != null ? file.getPath() : null);
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkRead(name);
}
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
fd = new FileDescriptor();
open(name);
}
//... ...
}
这段代码有两个重点:
- 有个FileDescriptor字段
- 构造函数最后调用了open(name)方法。
FileDescriptor类里最关键的是这个叫handle的字段。就是我们打开文件的句柄(handle)。
public final class FileDescriptor {
private int fd;
private long handle;
//... ...
}
而open()方法是个native方法。如下所示,内部就是简单调用了另一个系统方法fileOpen()。
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
Java_java_io_FileInputStream_open(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jstring path) {
fileOpen(env, this, path, fis_fd, O_RDONLY);
}
而Windows系统fileOpen()方法的作用就是:获得目标文件的句柄,并赋值给handle字段。
/*
env是一个指向JAVA本地方法环境的指针,它的作用大部分用来获取环境参数,比如当前线程。
this相信大家都不陌生,这就是指的当前FileInputStream的实例,只不过在C/C++环境中,它是jobject类型
path就是文件路径了,也是我们传进来的name参数
fid是FileInputStream类中fd属性的地址偏移量
flags是打开文件的方式,一般就是只读方式。
*/
void fileOpen(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jstring path, jfieldID fid, int flags)
{
jlong h = winFileHandleOpen(env, path, flags);//这一句话就得到了一个文件的句柄
if (h >= 0) {
SET_FD(this, h, fid);//这一句话就是将这个句柄赋给了FileDescriptor类的handle属性
}
}
所以打开一个文件的本质很简单,就是获得这个文件在系统中的“句柄”,然后根据这个句柄,顺藤摸瓜找到这个文件在磁盘上的物理地址。最后对磁盘进行读写。
新I/O
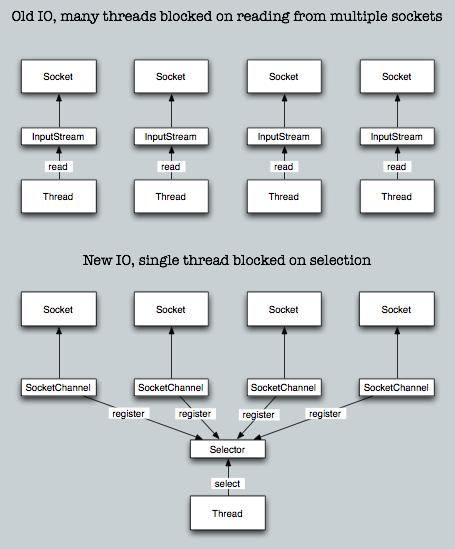
和老io包的 “面向流” 读写不同,引入java.nio包是 “面向缓冲区” 的读写。
什么是面向缓冲区?
“面向流”之前已经讲了,就是老IO包所有操作的的底层都是在InputStream和OutputStream的流上进行操作。上文已经分析过,比如我们打开文件,其实就是直接获取此文件在系统上的句柄,然后通过系统调用对文件进行读写。中间没有缓冲(BufferedReader那是通过装饰器套上的)。
而“面向缓冲区”的结构由两个部分组成:一个是管道“FileChannel”,一个是缓冲区“ByteBuffer”。他们两个就像是 “煤矿隧道” 和 “拉煤车” 的关系。至于样的模型为什么要比传统面向流的模型要高效,背后涉及两个不同的I/O模型。
传统阻塞式I/O
旧IO包采用的是传统阻塞式IO模式。如下图所示,阻塞式IO就是用户进程在系统调用读写文件时,保持“阻塞”。大白话讲就是知道文件完整地读写完之前,用户进程一直处在等待状态。
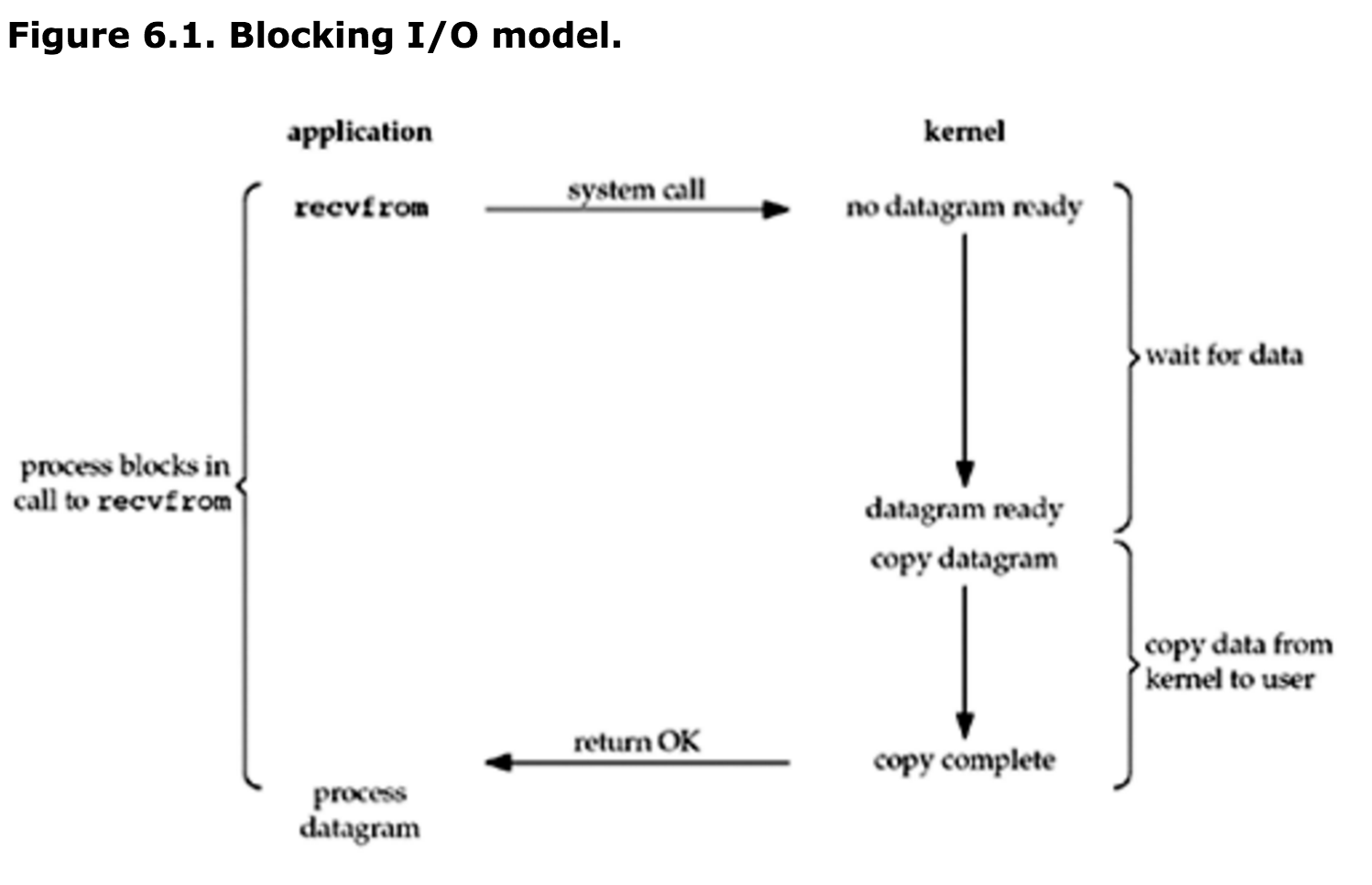
多路复用I/O
新IO采用的是复用I/O模型。简单讲就是第一个select步骤就是用户问系统他要的文件有没有准备好。之后的recvfrom才是真正的文件复制阶段。
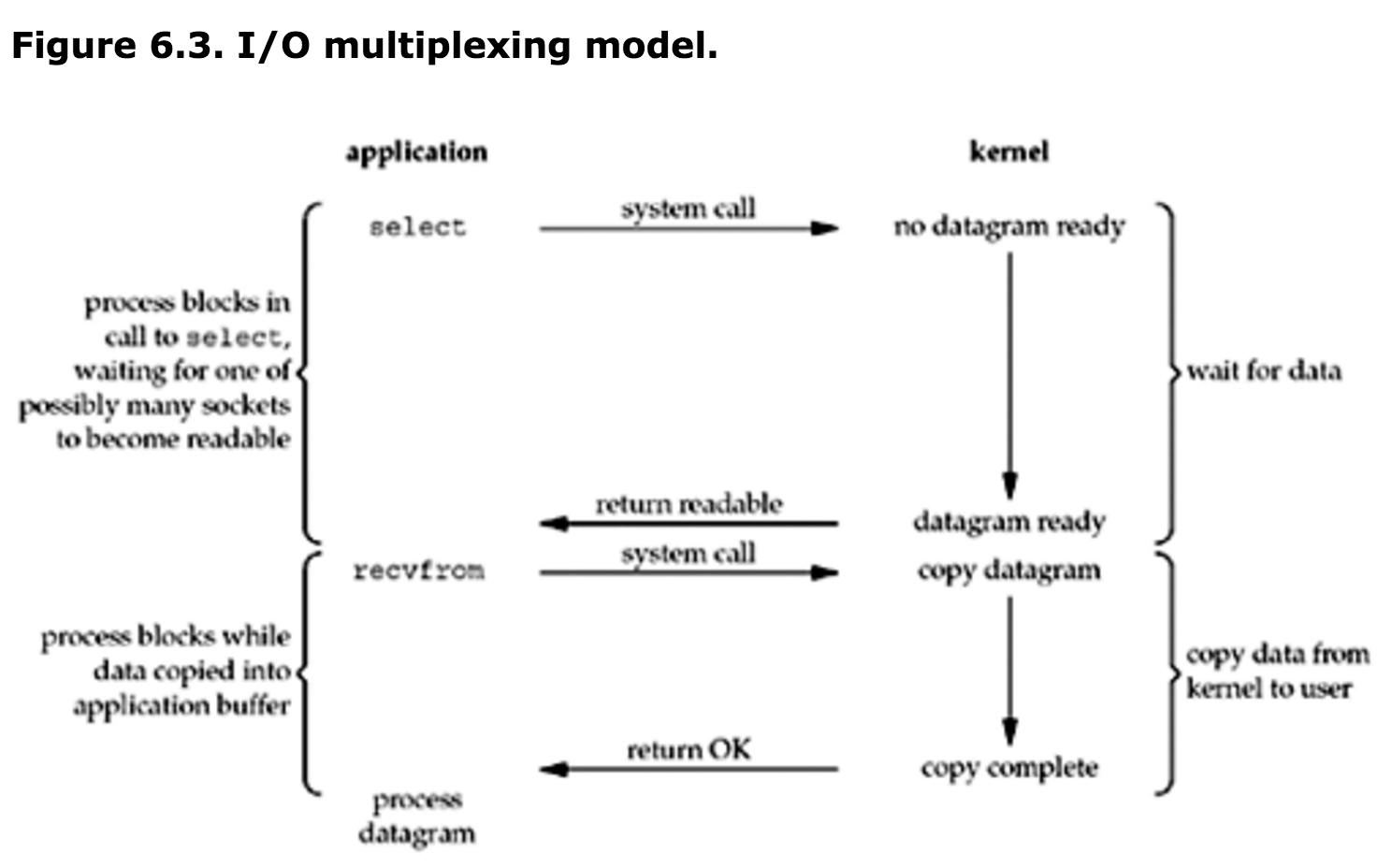
至于这个复用I/O模型好在哪儿,关键就在于它允许内核同时管理多条“管道”。最基本的是一个叫Reactor的模式。
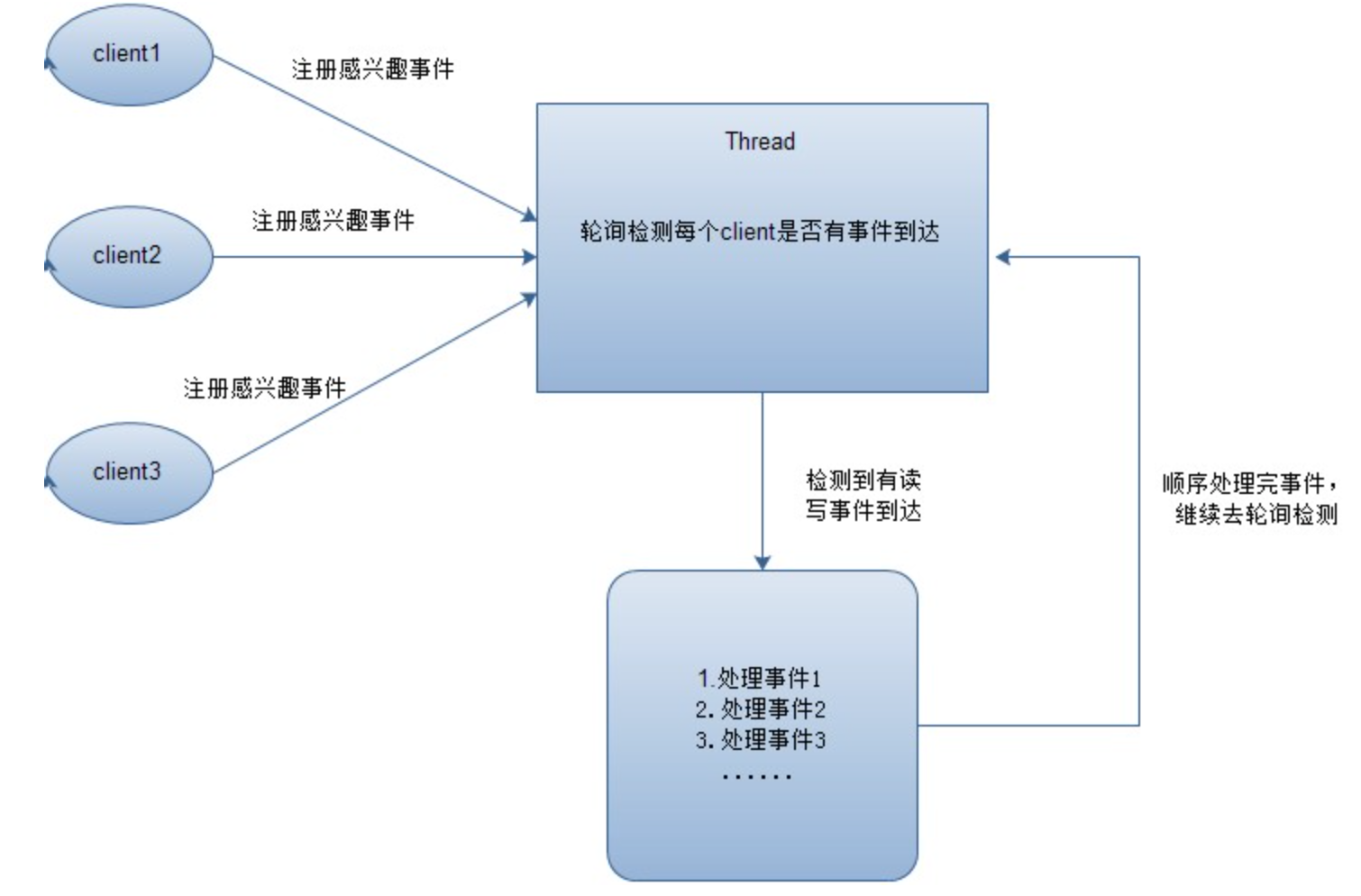
用户向内核注册感兴趣的事件(用register()方法),由内核维护一个负责轮询的线程,在某个同道准备好之后,通知用户。 nio多路复用的架构几乎就是UNIX内核的“管道-缓冲”架构的翻版。主要是为了更好地充分利用底层系统调用。实际上NIO在性能上已经几乎达到了它能达到的最佳性能。
两者的区别
一张图,看清旧io包和nio包的区别。映证了NIO使用了Reactor模式。
演示
注意FileChannel并没有实现SelectableChannel接口,因此不支持Selector。只有用于网络传输的ServerSocketChannel才实现了SelectableChannel接口。 下面这个清单演示了一次创建Channel,Selector,以及Channel向Selector注册感兴趣事件,获得注册钥的过程。
//创建Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//创建Channel
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.configureBlocking( false );
ServerSocket ss = ssc.socket();
InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress( ports[i] );
ss.bind( address );
//Channel向Selector注册感兴趣事件
SelectionKey key = ssc.register( selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT );
接下来,用Selector#selectedKey()方法监听发生的感兴趣事件,对返回的就绪的SelectionKey一一处理。
int num = selector.select();
Set selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator it = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey)it.next();
// ... deal with I/O event ...
}
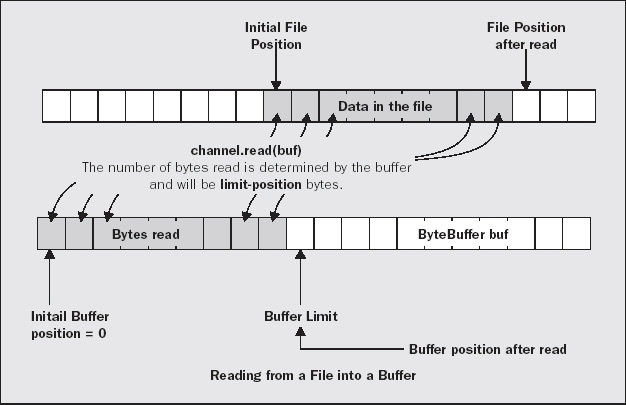
Buffer的细节
通过mark,position,limit,capacity四个标量控制缓冲区的读写。可以前进,可以后退,比传统流只能一位位往下读写更灵活。
MappedByteBuffer
一篇好文章:** 《深入浅出 MappedByteBuffer》 **
序列化
既然类和对象的本质就是数据的封装。那么无论是类还是对象,本质都是一组结构化的数据,也就是都可以序列化。
支持序列化的类必须实现 “Serializable” 接口。它只是一个标记性接口,没有定义任何方法。
一个序列化的对象可以被编码成流写入磁盘,“持久”储存。并且对象序列化保存的是对象的“全景图”和它所包含的所有引用。
对象序列化具体是一个很复杂的过程,尽量不要自己重复造轮子。用系统自带的 “ObjectOutputStream” 和 “ObjectInputStream” 就可以。
对象的“持久化”似乎为OO编程在工程上打开了一扇新的大门。尤其是网络编程,这让远距离传输对象变得非常方便。只要拥有某个类的.class文件,就能远距离复活这个类的对象。
- !注意:序列化有个“缺陷”,就是不能序列化静态字段。需要自己添加额外方法来实现追加序列化静态字段。就像 “练习30” 中演示的那样。
Externalizable接口
Externalizable接口继承自Serializable接口。可以在序列化和反序列化过程中提供更多的控制。
实现Externalizable接口的类在被反序列化的时候,不是直接通过字节码来全盘复制和重建对象,而是调用默认构造器,重新构造。
接口通过定义 WriteExternal(ObjectOutput out) 和 ReadExternal(ObjectInput in) 两个方法。分别接受输入,输出流为参数,目的是允许追加序列化某些需要被序列化的部件。所以更灵活。
transient关键字
transient 关键字用来“定点关闭”某些不想被序列化的“敏感字段”,比如说密码。
持久化的另一个选择 - Preferences API
要持久化某些数据或者部件,序列化并不是唯一的选择。另一种更轻量级的实现是Preferences API。
关于Prefecrences API的一篇文章:《用 Preferences API 存储对象》
它有点类似Windows的注册表。这里对它的细节深挖。但它确实可以在系统层面持久储存某些信息。比如基本型,以及String。但它只能做这么多。
数据结构层面,Preferences是一系列“键-值”对的节点。一共有两棵树”用户树”和”系统树“。分别用userNodeForPackage()和systemNodeForPackage()。这两棵树功能是一样的。
具体这些数据被储存到哪里了?对不同的操作系统,Java使用的是不同的系统资源。对于Windows系统,就是存在了注册表里。
练习
Exercise 1
- Exercise 1: (3) Modify DirList.java (or one of its variants) so that the FilenameFilter opens and reads each file (using the net.mindview.util.TextFile utility) and accepts the file based on whether any of the trailing arguments on the command line exist in that file.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise1 {
public static void main(final String[] args) {
File path = new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter17/testframework/gen/");
String[] list;
final String p;
if(args.length == 0){
p=".*gen.*";
}else{
p=args[0];
}
list = path.list(new FilenameFilter() {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(p);
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
boolean result=false;
try{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(dir.getAbsolutePath()+"/"+name)));
while(true){
String line=br.readLine();
if(line==null){break;}
if(pattern.matcher(line).matches()){
result=true;
}
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Can not open file: "+dir.getAbsolutePath()+name);
}
return result;
}
});
Arrays.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
for(String dirItem : list)
System.out.println(dirItem+": contains "+p);
}
}
Exercise 2
- Exercise 2: (2) Create a class called SortedDirList with a constructor that takes a File object and builds a sorted directory list from the files at that File. Add to this class two overloaded list( ) methods: the first produces the whole list, and the second produces the subset of the list that matches its argument (which is a regular expression).
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise2 {
public static class SortedDirList{
private File path;
private String[] list;
public SortedDirList(String absPath){
path=new File(absPath);
list = path.list();
}
public String[] list(){return list;}
public String[] list(String regex){
list = path.list(new FilenameFilter() {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return pattern.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
Arrays.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
return list;
}
}
public static void main(final String[] args) {
Exercise2.SortedDirList dl=new Exercise2.SortedDirList("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter17/testframework/gen/");
String[] fullList=dl.list();
String[] filteredList=dl.list(".*Ran.*");
System.out.println(">>>FULL LIST<<<\n"+Arrays.toString(fullList)+"\n");
System.out.println(">>>GEN LIST<<<\n"+Arrays.toString(filteredList));
}
}
Exercise 3
- Exercise 3: (3) Modify DirList.java (or one of its variants) so that it sums up the file sizes of the selected files.
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise3 {
public static class SortedDirList{
private File path;
private String[] list;
public SortedDirList(String absPath){
path=new File(absPath);
list = path.list();
}
public String[] list(){return list;}
public String[] list(String regex){
list = path.list(new FilenameFilter() {
private Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return pattern.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
Arrays.sort(list, String.CASE_INSENSITIVE_ORDER);
return list;
}
public File getPath(){return path;}
}
public static int countLine(File dir, String[] list){
if(list.length==0){return 0;}
int result=0;
for(String name:list){
try{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(dir+"/"+name)));
while(br.readLine()!=null){result++;}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("Can not open the file: "+dir+"/"+name);
}
}
return result;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) {
Exercise3.SortedDirList dl=new Exercise3.SortedDirList("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter17/testframework/gen/");
String[] fullList=dl.list();
String[] filteredList=dl.list(".*Ran.*");
System.out.println(">>>FULL LIST<<<\n"+Arrays.toString(fullList)+"\n");
System.out.println(">>>GEN LIST<<<\n"+Arrays.toString(filteredList)+"\n");
System.out.println("Total Line: "+Exercise3.countLine(dl.getPath(),filteredList));
}
}
Exercise 4,5,6
-
Exercise 4: (2) Use Directory.walk( ) to sum the sizes of all files in a directory tree whose names match a particular regular expression.
-
Exercise 5: (1) Modify ProcessFiles.java so that it matches a regular expression rather than a fixed extension.
-
Exercise 6: (5) Use ProcessFiles to find all the Java source-code files in a particular directory subtree that have been modified after a particular date.
Directory.java
简化练习4中的Directory类。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Directory{
private List<File> files=new ArrayList<File>();
private List<File> dirs=new ArrayList<File>();
private int size=0;
private int lines=0;
public Directory(){this(".");}
public Directory(String dir){this(new File(dir));}
public Directory(File dir){this(dir,".*");}
public Directory(String dir, String regex){this(new File(dir),regex);}
public Directory(File dir,String regex){
recurseDirs(dir,new FilenameFilter(){
private Pattern p=Pattern.compile(regex);
public boolean accept(File dir,String name){
return p.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
statistic();
}
public Directory(File dir,FilenameFilter filter){
recurseDirs(dir,filter);
statistic();
}
//递归收集文件
public void recurseDirs(File dir, FilenameFilter filter){
File[] children=dir.listFiles();
if(children==null || children.length==0){return;}
for(File f:children){
if(f.isDirectory()){
dirs.add(f);
recurseDirs(f,filter);
}else{
if(filter.accept(dir,f.getName())){
files.add(f);
}
}
}
}
public void statistic(){
if(files!=null && files.size()>0){
size=files.size();
int num=0;
for(File file:files){
try{
BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
while(bf.readLine()!=null){
num++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" can not open!");
}
}
lines=num;
}
}
public List<File> getFile(){return files;}
public List<File> getDir(){return dirs;}
public void showStatistic(){System.out.println("File number: "+size+"\n"+"Total Lines: "+lines+"\n");}
}
Exercise4.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise4{
public static void main(String[] args){
Directory d=new Directory("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter17/testframework/",".*Gen.*");
d.showStatistic();
List<File> files=d.getFile();
List<File> dirs=d.getDir();
if(files!=null && !(files.size()==0)){
System.out.println(files);
}
if(dirs!=null && !(dirs.size()==0)){
System.out.println(dirs);
}
}
}
ProcessFiles.java
ProcessFiles配合Directory使用。由Directory递归读取文件,然后由ProcessFiles里的Strategy模块处理。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class ProcessFiles {
public interface Strategy {
void process(File file);
}
private Strategy strategy;
private String ext;
public ProcessFiles(Strategy strategy, String ext) {
this.strategy = strategy;
this.ext = ext;
}
public void start(String[] args){
try{
if(args.length==0){
processDirectoryTree(new File("."));
}else{
for(String arg:args){
processDirectoryTree(new File(arg));
}
}
}catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void processDirectoryTree(File root) throws IOException {
for(File file : new Directory(root.getAbsolutePath(), ".*\\." + ext).getFile()){
strategy.process(file.getCanonicalFile());
}
}
// Demonstration of how to use it:
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ProcessFiles(new ProcessFiles.Strategy() {
public void process(File file) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}, "java").start(args);
}
}
Exercise5.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise5{
public static void main(String[] args){
new ProcessFiles(new ProcessFiles.Strategy() {
public void process(File file) {
System.out.println(file);
}
}, "ja.*").start(args);
}
}
}
Exercise6.java
用Directory和ProcessFile,对File做时间过滤。加了两个“时间-日期”转换方法。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.text.*;
public class Exercise6{
public static void filterByModifyDate(String[] args, String date){
new ProcessFiles(new ProcessFiles.Strategy() {
private long time=getNanoTime(date);
public void process(File file) {
if(file.lastModified()>time){
System.out.println(file+" >>>Last Modified: "+getFormatDate(file.lastModified()));
}
}
}, "java").start(args);
}
public static long getNanoTime(String date){
try{
DateFormat dateFormat1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date myDate = dateFormat1.parse(date);
return myDate.getTime();
}catch(ParseException pe){
System.out.println("Error when parsing Date!");
}
return 0l;
}
public static String getFormatDate(long millitime){
SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return df.format(millitime).toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
filterByModifyDate(args,"2016-09-29");
}
}
Exercise 7
- Exercise 7: (2) Open a text file so that you can read the file one line at a time. Read each line as a String and place that String object into a LinkedList. Print all of the lines in the LinkedList in reverse order.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise7{
public static void main(String[] args){
File file=new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Directory.java");
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
BufferedReader bf=null;
try{
bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
while(true){
String line=bf.readLine();
if(line==null){break;}
list.add(line);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" not found!");
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("have problem when reading lines... ...");
}finally{
if(bf!=null){
try{
bf.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("File can not be close!");
}
}
}
int size=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(--size));
}
}
}
Exercise 8
- Exercise 8: (1) Modify Exercise 7 so that the name of the file you read is provided as a command-line argument.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise8{
public static void inversePrint(File file){
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
BufferedReader bf=null;
try{
bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
while(true){
String line=bf.readLine();
if(line==null){break;}
list.add(line);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" not found!");
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("have problem when reading lines... ...");
}finally{
if(bf!=null){
try{
bf.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("File can not be close!");
}
}
}
int size=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(--size));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length==0){
Exercise8.inversePrint(new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Directory.java"));
}else{
for(String arg:args){
Exercise8.inversePrint(new File(arg));
}
}
}
}
Exercise 9
- Exercise 9: (1) Modify Exercise 8 to force all the lines in the LinkedList to uppercase and send the results to System.out.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise9{
public static void inversePrint(File file){
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
BufferedReader bf=null;
try{
bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
while(true){
String line=bf.readLine();
if(line==null){break;}
list.add(line.toUpperCase());
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" not found!");
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("have problem when reading lines... ...");
}finally{
if(bf!=null){
try{
bf.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("File can not be close!");
}
}
}
int size=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(--size));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length==0){
Exercise9.inversePrint(new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Directory.java"));
}else{
for(String arg:args){
Exercise9.inversePrint(new File(arg));
}
}
}
}
Exercise 10
- Exercise 10: (2) Modify Exercise 8 to take additional command-line arguments of words to find in the file. Print all lines in which any of the words match.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Exercise10{
public static void inversePrint(File file, String inWord){
LinkedList<String> list=new LinkedList<String>();
BufferedReader bf=null;
try{
bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line=null;
while((line=bf.readLine())!=null){
String[] words=line.split("[\\W]+");
if(words.length>0){
for(String word:words){
if(word.toLowerCase().equals(inWord)){
list.add(line);
break;
}
}
}
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" not found!");
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("have problem when reading lines... ...");
}finally{
if(bf!=null){
try{
bf.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("File can not be close!");
}
}
}
int size=list.size();
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
System.out.println(list.get(--size));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length!=2){
System.out.println("Please check the args!");
}else{
Exercise10.inversePrint(new File(args[0]),args[1]);
}
}
}
Exercise 11
- Exercise 11: (2) In the innerclasses/GreenhouseController.java example, GreenhouseController contains a hard-coded set of events. Change the program so that it reads the events and their relative times from a text file, ((difficulty level 8): Use a Factory Method design pattern to build the events.
使用了注册工厂模式。
Controller.java
基层设施
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public class Controller {
// A class from java.util to hold Event objects:
private List<Event> eventList = new ArrayList<Event>();
public void addEvent(Event c) { eventList.add(c); }
public void run() {
while(eventList.size() > 0)
// Make a copy so you’re not modifying the list
// while you’re selecting the elements in it:
for(Event e : new ArrayList<Event>(eventList))
if(e.ready()) {
System.out.println(e);
e.action();
eventList.remove(e);
}
}
public List<Event> getList(){return eventList;}
}
Event.java
基层设施
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public abstract class Event {
private long eventTime;
protected final long delayTime;
public Event(long delayTime) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
start();
}
public void start() { // Allows restarting
eventTime = System.nanoTime() + delayTime;
}
public boolean ready() {
return System.nanoTime() >= eventTime;
}
public abstract void action();
}
GreenhouseControls.java
Controller和Event的综合体。 内部有一个Controller字段,每个Event都是一个内部类。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public class GreenhouseControls {
private static Controller con=new Controller();
public Controller getController(){return con;}
private static boolean light = false;
public static class LightOn extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<LightOn>{
public LightOn create(long delayTime){return new LightOn(delayTime);}
}
public LightOn(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here to
// physically turn on the light.
light = true;
}
public String toString() { return "Light is on"; }
}
public static class LightOff extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<LightOff>{
public LightOff create(long delayTime){return new LightOff(delayTime);}
}
public LightOff(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here to
// physically turn off the light.
light = false;
}
public String toString() { return "Light is off"; }
}
private static boolean water = false;
public static class WaterOn extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<WaterOn>{
public WaterOn create(long delayTime){return new WaterOn(delayTime);}
}
public WaterOn(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
water = true;
}
public String toString() {
return "Greenhouse water is on";
}
}
public static class WaterOff extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<WaterOff>{
public WaterOff create(long delayTime){return new WaterOff(delayTime);}
}
public WaterOff(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
water = false;
}
public String toString() {
return "Greenhouse water is off";
}
}
private static String thermostat = "Day";
public static class ThermostatNight extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<ThermostatNight>{
public ThermostatNight create(long delayTime){return new ThermostatNight(delayTime);}
}
public ThermostatNight(long delayTime) {
super(delayTime);
}
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
thermostat = "Night";
}
public String toString() {
return "Thermostat on night setting";
}
}
public static class ThermostatDay extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<ThermostatDay>{
public ThermostatDay create(long delayTime){return new ThermostatDay(delayTime);}
}
public ThermostatDay(long delayTime) {
super(delayTime);
}
public void action() {
// Put hardware control code here.
thermostat = "Day";
}
public String toString() {
return "Thermostat on day setting";
}
}
// An example of an action() that inserts a
// new one of itself into the event list:
public static class Bell extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<Bell>{
public Bell create(long delayTime){return new Bell(delayTime);}
}
public Bell(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() {
con.addEvent(new Bell(delayTime));
}
public String toString() { return "Bing!"; }
}
public static class Restart extends Event {
public static class Factory implements BigEventFactory<Restart>{
public Restart create(long delayTime, Event[] eventList){return new Restart(delayTime, eventList);}
}
private Event[] eventList;
public Restart(long delayTime, Event[] eventList) {
super(delayTime);
this.eventList = eventList;
for(Event e : eventList)
con.addEvent(e);
}
public void action() {
for(Event e : eventList) {
e.start(); // Rerun each event
con.addEvent(e);
}
start(); // Rerun this Event
con.addEvent(this);
}
public String toString() {
return "Restarting system";
}
}
public static class Terminate extends Event {
public static class Factory implements SmallEventFactory<Terminate>{
public Terminate create(long delayTime){return new Terminate(delayTime);}
}
public Terminate(long delayTime) { super(delayTime); }
public void action() { System.exit(0); }
public String toString() { return "Terminating"; }
}
}
EventFactory.java
工厂接口
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public interface EventFactory<T>{}
BigEventFactory.java
工厂接口。因为Restart类的create()方法有两个参数,所以分化出一个工厂类。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public interface BigEventFactory<T>{
public T create(long delayTime, Event[] eventList);
}
SmallEventFactory.java
工厂接口。正常Event的工厂接口。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public interface SmallEventFactory<T>{
public T create(long delayTime);
}
ControllerHelper.java
主要是Event的注册工厂。还有一个从外部文件读取EventList的loadEvents()方法。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class ControllerHelper {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static Map<String,SmallEventFactory<? extends Event>> smallEventFactories=new HashMap<String,SmallEventFactory<? extends Event>>();
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
private static Map<String,BigEventFactory<? extends Event>> bigEventFactories=new HashMap<String,BigEventFactory<? extends Event>>();
static {
smallEventFactories.put("LightOn",new GreenhouseControls.LightOn.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("LightOff",new GreenhouseControls.LightOff.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("WaterOn",new GreenhouseControls.WaterOn.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("WaterOff",new GreenhouseControls.WaterOff.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("ThermostatNight",new GreenhouseControls.ThermostatNight.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("ThermostatDay",new GreenhouseControls.ThermostatDay.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("Bell",new GreenhouseControls.Bell.Factory());
bigEventFactories.put("Restart",new GreenhouseControls.Restart.Factory());
smallEventFactories.put("Terminate",new GreenhouseControls.Terminate.Factory());
}
public static Event[] loadEvents(String path){
File file=new File(path);
List<Event> list=new ArrayList<Event>();
BufferedReader bf=null;
try{
bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String line=null;
while((line=bf.readLine())!=null){
String[] param=line.split("\\t");
if(param.length!=2){
System.out.println("Args Error: "+line);
}else{
System.out.println(param[0]+","+param[1]);
list.add(smallEventFactories.get(param[0]).create(Integer.parseInt(param[1])));
}
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" not found!");
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("have problem when reading lines... ...");
}finally{
if(bf!=null){
try{
bf.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("File can not be close!");
}
}
}
System.out.println(list);
return list.toArray(new Event[list.size()]);
}
}
Exercise11.java
最后的测试类。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
public class Exercise11{
public static void main(String[] args){
GreenhouseControls c=new GreenhouseControls();
Controller controller=c.getController();
controller.addEvent((Event)(ControllerHelper.smallEventFactories.get("Bell").create(900)));
Event[] eventList = ControllerHelper.loadEvents("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Event.txt");
controller.addEvent((Event)(ControllerHelper.bigEventFactories.get("Restart").create(2000,eventList)));
controller.addEvent((Event)(ControllerHelper.smallEventFactories.get("Terminate").create(1000)));
controller.run();
}
}
Exercise 12
- Exercise 12: (3) Modify Exercise 8 to also open a text file so you can write text into it. Write the lines in the LinkedList, along with line numbers (do not attempt to use the “LineNumber” classes), out to the file.
Exercise12.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise12{
public static void copyFile(File inFile, File outFile){
BufferedReader in=null;
PrintWriter out=null;
try{
//input
in=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inFile));
//output
if(!outFile.exists()){
outFile.createNewFile();
}
out=new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outFile)));
int count=0;
String line;
while((line=in.readLine())!=null){
out.println("Line "+ ++count +":\t"+line);
}
}catch(IOException ioe){
System.out.println("Check your inFile and outFile!");
}finally{
try{
in.close();
out.close();
}catch(IOException e){
System.out.println("Files cannot be closed correctly!");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
if(args.length!=2){
System.out.println("Check your arguments!");
}else{
copyFile(new File(args[0]), new File(args[1]));
}
}
}
Exercise 13
- Exercise 13: (3) Modify BasicFileOutput.java so that it uses LineNumberReader to keep track of the line count. Note that it’s much easier to just keep track programmatically.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise13 {
static String file = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/BasicFileOutput.txt";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
LineNumberReader in = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader(new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise13.java")));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file)));
int lineCount = 1;
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null ){
out.println(in.getLineNumber() + ": " + s);
}
out.close();
}
}
Exercise 14
- Exercise 14: (2) Starting with BasicFileOutput.java, write a program that compares the performance of writing to a file when using buffered and unbuffered I/O.
实验结果显示加了BufferedWriter装饰器之后比原先FileWriter效率高了20-25%。
需要当心,不要把最初两次测试结果统计进最后结果。因为最初的两轮耗时明显地长,尤其是第一次跑,是明显的离群点。这会导致先跑的Writer吃亏。
Exercise14.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise14 {
private static String inFile = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/BufferedInputFile.java";
public static long test(Writer out) throws IOException{
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(inFile)));
int lineCount = 1;
String s;
long begin;
long end;
long result=0;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null ){
begin=System.nanoTime();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
out.write(lineCount++ + ": " + s);
}
result+=(System.nanoTime()-begin);
}
out.close();
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long timeBuffer=0;
long timeNot=0;
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
FileWriter fileOut=new FileWriter("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/BufferedInputFile.txt");
BufferedWriter bufferedOut = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/BufferedInputFile2.txt"));
if(i>=5){
timeBuffer+=test(bufferedOut);
timeNot+=test(fileOut);
}
}
System.out.println("Buf: "+timeBuffer/15);
System.out.println("Not: "+timeNot/15);
System.out.println((double)timeBuffer/timeNot);
}
}
测试结果
Buf: 27568796
Not: 37021046
0.7446790010523365
Exercise 15
- Exercise 15: (4) Look up DataOutputStream and DataInputStream in the JDK documentation. Starting with StoringAndRecoveringData.java, create a program that stores and then retrieves all the different possible types provided by the DataOutputStream and DataInputStream classes. Verify that the values are stored and retrieved accurately.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise15 {
public static void write(String file) throws IOException{
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file)));
out.writeBoolean(true);
out.writeByte(56);
out.writeChar('a');
out.writeInt(56);
out.writeLong(56l);
out.writeShort(56);
out.writeFloat(56f);
out.writeDouble(3.14159);
out.writeUTF("That was pi");
out.close();
}
public static void read(String file) throws IOException{
DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file)));
boolean b=in.readBoolean();
byte bt=in.readByte();
char c=in.readChar();
int i=in.readInt();
long l=in.readLong();
short s=in.readShort();
float f=in.readFloat();
double d=in.readDouble();
String str=in.readUTF();
in.close();
System.out.println("["+b+"],"+"["+bt+"],"+"["+c+"],"+"["+i+"],"+"["+l+"],"+"["+s+"],"+"["+f+"],"+"["+d+"],"+"["+str+"]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String file="/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Data.txt";
write(file);
read(file);
}
}
Exercise 16
- Exercise 16: (2) Look up RandomAccessFile in the JDK documentation. Starting with UsingRandomAccessFile.java, create a program that stores and then retrieves all the different possible types provided by the RandomAccessFile class. Verify that the values are stored and retrieved accurately.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise16 {
static String file = "/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Data2.txt";
static void display() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile in = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
System.out.println("Value " + i + ": " + in.readDouble());
}
System.out.println(in.readUTF());
boolean b=in.readBoolean();
byte bt=in.readByte();
char c=in.readChar();
int i=in.readInt();
long l=in.readLong();
short s=in.readShort();
float f=in.readFloat();
double d=in.readDouble();
String str=in.readUTF();
in.close();
System.out.println("["+b+"],"+"["+bt+"],"+"["+c+"],"+"["+i+"],"+"["+l+"],"+"["+s+"],"+"["+f+"],"+"["+d+"],"+"["+str+"]");
}
static void write() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile out = new RandomAccessFile(file, "rw");
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
out.writeDouble(i*1.414);
}
out.writeUTF("The end of the file");
out.writeBoolean(true);
out.writeByte(56);
out.writeChar('a');
out.writeInt(56);
out.writeLong(56l);
out.writeShort(56);
out.writeFloat(56f);
out.writeDouble(3.14159);
out.writeUTF("That was pi");
out.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
write();
display();
}
}
Exercise 17
- Exercise 17: (4) Using TextFile and a Map<Character,Integer>, create a program that counts the occurrence of all the different characters in a file. (So if there are 12 occurrences of the letter ‘a’ in the file, the Integer associated with the Character containing ‘a’ in the Map contains ‘12’).
TextFile.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class TextFile extends ArrayList<String> {
// 读文件,返回String
public static String read(String fileName) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try {
BufferedReader in= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile()));
try {
String s;
while((s = in.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(s);
sb.append("\n");
}
} finally {
in.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// 直接写String进文件
public static void write(String fileName, String text) {
try {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try {
out.print(text);
} finally {
out.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 构造器。 切割成String的ArrayList。
public TextFile(String fileName, String splitter) {
super(Arrays.asList(read(fileName).split(splitter)));
if(get(0).equals("")){remove(0);}
}
// 构造器。按行切割。
public TextFile(String fileName) {
this(fileName, "\n");
}
public void write(String fileName) {
try {
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try {
for(String item : this){
out.println(item);
}
} finally {
out.close();
}
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String file = read("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.java");
write("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.txt", file);
TextFile text = new TextFile("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.txt");
text.write("test2.txt");
// Break into unique sorted list of words:
TreeSet<String> words = new TreeSet<String>(new TextFile("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.java", "\\W+"));
// Display the capitalized words:
System.out.println(words.headSet("a"));
}
}
Exercise17.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise17{
public static void main(String[] args){
TextFile tf=new TextFile("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.java","");
Map<Character, Integer> map=new HashMap<Character,Integer>();
for(String s:tf){
Character c=s.charAt(0);
if(map.containsKey(c)){
map.put(c,map.get(c)+1);
}else{
map.put(c,1);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Exercise 18
- Exercise 18: (1) Modify TextFile.java so that it passes IOExceptions out to the caller.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Exercise18 extends ArrayList<String> {
// 读文件,返回String
public static String read(String fileName) throws IOException{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
BufferedReader in= new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile()));
String s;
try{
while((s = in.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(s);
sb.append("\n");
}
}finally{
in.close();
}
return sb.toString();
}
// 直接写String进文件
public static void write(String fileName, String text) throws IOException{
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try{
out.print(text);
}finally{
out.close();
}
}
// 构造器。 切割成String的ArrayList。
public Exercise18(String fileName, String splitter) throws IOException{
super(Arrays.asList(read(fileName).split(splitter)));
if(get(0).equals("")){remove(0);}
}
// 构造器。按行切割。
public Exercise18(String fileName) throws IOException{
this(fileName, "\n");
}
public void write(String fileName) throws IOException{
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new File(fileName).getAbsoluteFile());
try{
for(String item : this){
out.println(item);
}
}finally{
out.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
String file = read("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.java");
write("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.txt", file);
Exercise18 text = new Exercise18("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.txt");
text.write("test2.txt");
// Break into unique sorted list of words:
TreeSet<String> words = new TreeSet<String>(new TextFile("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/TextFile.java", "\\W+"));
// Display the capitalized words:
System.out.println(words.headSet("a"));
}
}
Exercise 19
- Exercise 19: (2) Using BinaryFile and a Map<Byte,Integer>, create a program that counts the occurrence of all the different bytes in a file.
BinaryFile.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BinaryFile {
public static byte[] read(File bFile) throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bf = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(bFile));
try {
byte[] data = new byte[bf.available()];
bf.read(data);
return data;
} finally {
bf.close();
}
}
public static byte[] read(String bFile) throws IOException {
return read(new File(bFile).getAbsoluteFile());
}
}
Exercise19.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise19 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
byte[] bytes=BinaryFile.read("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/BinaryFile.java");
Map<Byte,Integer> map=new HashMap<Byte,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<bytes.length;i++){
byte b=bytes[i];
if(map.containsKey(b)){
map.put(b,map.get(b)+1);
}else{
map.put(b,1);
}
}
System.out.println(map);
}
}
Exercise 20
- Exercise 20: (4) Using Directory.walk( ) and BinaryFile, verify that all .class files in a directory tree begin with the hex characters ‘CAFEBABE’.
Directory.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
public class Directory{
private List<File> files=new ArrayList<File>();
private List<File> dirs=new ArrayList<File>();
private int size=0;
private int lines=0;
public Directory(){this(".");}
public Directory(String dir){this(new File(dir));}
public Directory(File dir){this(dir,".*");}
public Directory(String dir, String regex){this(new File(dir),regex);}
public Directory(File dir,String regex){
recurseDirs(dir,new FilenameFilter(){
private Pattern p=Pattern.compile(regex);
public boolean accept(File dir,String name){
return p.matcher(name).matches();
}
});
statistic();
}
public Directory(File dir,FilenameFilter filter){
recurseDirs(dir,filter);
statistic();
}
//递归收集文件
public void recurseDirs(File dir, FilenameFilter filter){
File[] children=dir.listFiles();
if(children==null || children.length==0){return;}
for(File f:children){
if(f.isDirectory()){
dirs.add(f);
recurseDirs(f,filter);
}else{
if(filter.accept(dir,f.getName())){
files.add(f);
}
}
}
}
public void statistic(){
if(files!=null && files.size()>0){
size=files.size();
int num=0;
for(File file:files){
try{
BufferedReader bf=new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
while(bf.readLine()!=null){
num++;
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(file.getName()+" can not open!");
}
}
lines=num;
}
}
public List<File> getFile(){return files;}
public List<File> getDir(){return dirs;}
public void showStatistic(){System.out.println("File number: "+size+"\n"+"Total Lines: "+lines+"\n");}
}
BinaryFile.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class BinaryFile {
public static byte[] read(File bFile) throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bf = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(bFile));
try {
byte[] data = new byte[bf.available()];
bf.read(data);
return data;
} finally {
bf.close();
}
}
public static byte[] read(String bFile) throws IOException {
return read(new File(bFile).getAbsoluteFile());
}
}
Exercise20.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise20 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Directory dir=new Directory("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18");
List<File> files=dir.getFile();
if(!files.isEmpty()){
for(File file:files){
if(file.getName().endsWith(".class")){
byte[] bytes=BinaryFile.read(file);
String one=Integer.toHexString(((Byte)bytes[0]).intValue());
String two=Integer.toHexString(((Byte)bytes[1]).intValue());
String three=Integer.toHexString(((Byte)bytes[2]).intValue());
String four=Integer.toHexString(((Byte)bytes[3]).intValue());
System.out.println(one+two+three+four);
}
}
}
}
}
Exercise 21
- Exercise 21: (1) Write a program that takes standard input and capitalizes all characters, then puts the results on standard output. Redirect the contents of a file into this program (the process of redirection will vary depending on your operating system).
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise21{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
PrintStream console=System.out;
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintStream ps=new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise21.txt")));
System.setOut(ps);
String s;
while((s=br.readLine())!=null && s.length()!=0){
s=s.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
}
ps.close();
System.setOut(console);
}
}
Exercise 22
- Exercise 22: (5) Modify OSExecute.java so that, instead of printing the standard output stream, it returns the results of executing the program as a List of Strings. Demonstrate the use of this new version of the utility.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Exercise22 {
public static List<String> command(String command) {
boolean err = false;
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
try {
Process process = new ProcessBuilder(command.split(" ")).start();
BufferedReader results = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getInputStream()));
String s;
while((s = results.readLine())!= null){
list.add(s);
}
BufferedReader errors = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(process.getErrorStream()));
// Report errors and return nonzero value
// to calling process if there are problems:
while((s = errors.readLine())!= null) {
System.err.println(s);
err = true;
}
} catch(Exception e) {
// Compensate for Windows 2000, which throws an
// exception for the default command line:
if(!command.startsWith("CMD /C")){
command("CMD /C " + command);
}else{
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(err){
throw new OSExecuteException("Errors executing " + command);
}
return list;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
List<String> reverse=Exercise22.command("javap com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18.OSExecute");
System.out.println(reverse);
}
}
Exercise 23
- Exercise 23: (6) Create and test a utility method to print the contents of a CharBuffer up to the point where the characters are no longer printable.
这题有个坑: asCharBuffer()方法,默认以UTF-16BE来解码byteBuffer里的字节。每个字符2字节。而String # getBytes()使用我系统默认编码方式:而我系统的默认编码方式是:UTF-8。英语字母一个字节。
- 解决方法一:要么在byte解码到char的时候,找到系统默认的编码标准。
- 解决方法二:要么在getBytes编码的时候就用asCharSet默认的UTF-16BE标准:getBytes(“UTF-16BE”)。
- 解决方法三:要么在写入文件的时候直接用CharSet的视图往里写入,就会直接用UTF-16BE的编码标准。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
public class Exercise23{
private static final int BSIZE=1024;
private File f;
public Exercise23(String s) throws IOException{
this(new File(s));
}
public Exercise23(File f) throws IOException{
this.f=f;
if(!f.exists()){
f.createNewFile();
}
}
public void write(String s) throws IOException{
FileChannel fc=new FileOutputStream(f).getChannel();
//method 1 to create and fill a ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer bf1=ByteBuffer.wrap(s.substring(0,s.length()/2).getBytes());
//method 2 to create and fill a ByteBuffer
ByteBuffer bf2=ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
bf2.put(s.substring(s.length()/2).getBytes());
bf2.flip(); //Important!!
fc.write(bf1);
fc.write(bf2);
fc.close();
}
public byte[] read() throws IOException{
FileChannel fc=new FileInputStream(f).getChannel();
ByteBuffer bf=ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
fc.read(bf);
bf.flip();
byte[] ba=new byte[bf.limit()];
int index=0;
while(bf.hasRemaining()){
ba[index]=bf.get();
index++;
}
fc.close();
return ba;
}
//输出乱码
public char[] badReadAsChars() throws IOException{
FileChannel fc=new FileInputStream(f).getChannel();
ByteBuffer bf=ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
fc.read(bf);
bf.flip();
/**
* 坑在这儿:
* asCharBuffer()方法,默认以UTF-16BE来解码byteBuffer里的字节。每个字符2字节。
* 而String # getBytes()使用我系统默认编码方式:
* 而我系统的默认编码方式是:UTF-8。英语字母一个字节。
*/
CharBuffer cf=bf.asCharBuffer();
char[] ca=new char[cf.limit()];
int index=0;
while(cf.hasRemaining()){
ca[index]=cf.get();
index++;
}
fc.close();
return ca;
}
//这种解决方案比较好。因为从头到尾使用系统默认的编码标准,系统打开本地写入的文件的时候,不会显示乱码。
public char[] readAsChars() throws IOException{
FileChannel fc=new FileInputStream(f).getChannel();
ByteBuffer bf=ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
fc.read(bf);
bf.flip();
//解决方法一
//要么在byte解码到char的时候,找到系统默认的编码标准。
CharBuffer cf=Charset.forName(System.getProperty("file.encoding")).decode(bf);
char[] ca=new char[cf.limit()];
int index=0;
while(cf.hasRemaining()){
ca[index]=cf.get();
index++;
}
fc.close();
return ca;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//系统默认编码是UTF-8
System.out.println(System.getProperty("file.encoding"));
Exercise23 gc=new Exercise23("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise23.txt");
gc.write("Hello World!");
byte[] ba=gc.read();
System.out.println("Bytes >>> "+Arrays.toString(ba));
System.out.println("String >>> "+new String(ba));
char[] ca=gc.readAsChars();
System.out.println("Chars >>> "+Arrays.toString(ca));
System.out.println("String >>> "+new String(ca));
}
}
Exercise 24
- Exercise 24: (1) Modify IntBufferDemo.java to use doubles.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
public class Exercise24{
private static final int BSIZE = 1024;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
DoubleBuffer db = bb.asDoubleBuffer();
db.put(new double[]{ 11.1, 42.2, 47.3, 99.4, 143.5, 811.6, 1016.7 });
System.out.println(db.get(3));
db.put(new double[] {3.8, 1811.9});
db.flip();
while(db.hasRemaining()) {
double d = db.get();
System.out.println(d);
}
}
}
Exercise 25
- Exercise 25: (6) Experiment with changing the ByteBuffer.allocate( ) statements in the examples in this chapter to ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( ). Demonstrate performance differences, but also notice whether the startup time of the programs noticeably changes.
确实如书中所说,ByteBuffer.allocateDirect()可以提高后面的读写效率,但allocateDirect()本身启动时间比allocate()慢。
Exercise25.java
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
public class Exercise25{
private static final int BSIZE = 1048576;
private abstract static class Tester {
private String name;
public Tester(String name) { this.name = name; }
public void runTest() {
System.out.print(name + ": ");
try {
long start = System.nanoTime();
long mid=test();
long end=System.nanoTime();
double firstHalf = mid-start;
double secondHalf = end - mid;
System.out.format("%.2f %.2f\n", firstHalf/1.0e6, secondHalf/1.0e6);
} catch(IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public abstract long test() throws IOException;
}
private static Tester[] tests={
new Tester("Allocate") {
public long test() throws IOException{
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocate(BSIZE);
long mid=System.nanoTime();
DoubleBuffer db = bb.asDoubleBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<BSIZE/8;i++){
db.put((double)i);
}
return mid;
}
},
new Tester("AllocateDirect") {
public long test() throws IOException{
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(BSIZE);
long mid=System.nanoTime();
DoubleBuffer db = bb.asDoubleBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<BSIZE/8;i++){
db.put((double)i);
}
return mid;
}
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(Tester test : tests){
test.runTest();
}
}
}
结果
Allocate: 0,62 10,53
AllocateDirect: 0,96 4,52
Exercise 26
- Exercise 26: (3) Modify strings/JGrep.java to use Java nio memorymapped files.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
import java.nio.channels.*;
import java.nio.charset.*;
public class Exercise26{
public static void jgrep(String regex, String path) throws IOException{
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);
// Iterate through the lines of the input file:
int index = 0;
Matcher m = p.matcher("");
FileChannel fc=new RandomAccessFile(path, "r").getChannel();
CharBuffer cb=Charset.forName(System.getProperty("file.encoding")).decode(fc.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, fc.size()));
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
Character c;
while(cb.hasRemaining()){
c=cb.get();
sb.append(c);
if(c.equals('\n')){
m.reset(sb.toString());
while(m.find()){
System.out.println(index++ + ": " + m.group() + ": " + m.start());
}
sb.delete(0,sb.length());
}
}
fc.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
jgrep("if","/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise26.java");
}
}
Exercise 27
- Exercise 27: (1) Create a Serializable class containing a reference to an object of a second Serializable class. Create an instance of your class, serialize it to disk, then restore it and verify that the process worked correctly.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
public class Exercise27{
private static Random rander=new Random();
public static class Pregnant implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private int month;
private Baby theBaby;
public Pregnant(int month){
this.month=month;
theBaby=new Baby(month);
}
public String toString(){return "Pregnant for "+month+" month! Baby weights "+theBaby.getWeight()+" KG!";}
}
public static class Baby implements Serializable{
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private float weight;
private int sex;
public Baby(int month){
weight=rander.nextFloat()*rander.nextInt(2)+(float)month;
sex=rander.nextInt(1);
}
public float getWeight(){return weight;}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException{
Exercise27.Pregnant p=new Pregnant(5);
File f=new File("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise27.txt");
if(!f.exists()){
f.createNewFile();
}
//序列化
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
out.writeObject(p);
//反序列化
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
Pregnant p2=(Pregnant)in.readObject();
System.out.println(p2);
}
}
Exercise 28
- Exercise 28 : (2) In Blips.java, copy the file and rename it to BlipCheck.java and rename the class Blip2 to BlipCheck (making it public and removing the public scope from the class Blips in the process). Remove the //! marks in the file and execute the program, including the offending lines. Next, comment out the default constructor for BlipCheck. Run it and explain why it works. Note that after compiling, you must execute the program with “Java Blips” because the main( ) method is still in the class Blips.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
public class Exercise28 {
public static class BlipCheck implements Externalizable {
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
//这里默认构造器会被外部调用,所以必须是public的。
//注释掉之后系统会自动创建一个默认构造器,默认是public的。
/*
BlipCheck() {
System.out.println("Blip2 Constructor");
}
*/
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Blip2.writeExternal");
}
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("Blip2.readExternal");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("Constructing objects:");
Exercise28.BlipCheck bc = new Exercise28.BlipCheck();
ObjectOutputStream o = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise28.txt"));
System.out.println("Saving objects:");
o.writeObject(bc);
o.close();
// Now get them back:
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise28.txt"));
System.out.println("Recovering BlipCheck:");
bc = (BlipCheck)in.readObject();
}
}
Exercise 29
- Exercise 29: (2) In Blip3.java, comment out the two lines after the phrases “You must do this:” and run the program. Explain the result and why it differs from when the two lines are in the program.
运行的结果会抛出OptionalDataException。异常的原因是实现Externalizable接口的可序列化类,在序列化和反序列化的时候,都只调用默认的构造器。而这里Blip3的默认构造器没有初始化s和i的值。而在writeExternal和readExternal方法里又没有把s和i补偿序列化。反序列化的结果不完整。s和i始终没有初始化。
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
public class Exercise29 {
public static class Blip3 implements Externalizable {
private static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
private int i;
private String s; // No initialization
public Blip3() {
System.out.println("Blip3 Constructor");
// s, i not initialized
}
public Blip3(String x, int a) {
System.out.println("Blip3(String x, int a)");
s = x;
i = a;
// s & i initialized only in non-default constructor.
}
public String toString() { return s + i; }
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
System.out.println("Blip3.writeExternal");
// You must do this:
//out.writeObject(s);
//out.writeInt(i);
}
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("Blip3.readExternal");
// You must do this:
s = (String)in.readObject();
i = in.readInt();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("Constructing objects:");
Exercise29.Blip3 b3 = new Exercise29.Blip3("A String ", 47);
System.out.println(b3);
ObjectOutputStream o = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise29.txt"));
System.out.println("Saving object:");
o.writeObject(b3);
o.close();
// Now get it back:
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/Exercise29.txt"));
System.out.println("Recovering b3:");
b3 = (Blip3)in.readObject();
// System.out.println(b3); //!!OptionalDataException
}
}
Exercise 30
- Exercise 30: (1) Repair the program CADState.java as described in the text.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.*;
public class Exercise30 {
public abstract static class Shape implements Serializable {
protected static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
public static final int RED = 1, BLUE = 2, GREEN = 3;
public static int color=0;
private int xPos, yPos, dimension;
private static Random rand = new Random(47);
private static int counter = 0;
public abstract void setColor(int newColor);
public abstract int getColor();
public Shape(int xVal, int yVal, int dim) {
xPos = xVal;
yPos = yVal;
dimension = dim;
}
public String toString() {
return getClass() +
"color[" + getColor() + "] xPos[" + xPos +
"] yPos[" + yPos + "] dim[" + dimension + "]\n";
}
public static Shape randomFactory() {
int xVal = rand.nextInt(100);
int yVal = rand.nextInt(100);
int dim = rand.nextInt(100);
switch(counter++ % 3) {
default:
case 0: return new Circle(xVal, yVal, dim);
case 1: return new Square(xVal, yVal, dim);
case 2: return new Line(xVal, yVal, dim);
}
}
public static void serializeStaticState(ObjectOutputStream os) throws IOException { os.writeInt(color); }
public static void deserializeStaticState(ObjectInputStream os) throws IOException { color = os.readInt(); }
}
public static class Circle extends Shape {
protected static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
public Circle(int xVal, int yVal, int dim) {
super(xVal, yVal, dim);
color=RED;
}
public void setColor(int newColor) { color = newColor; }
public int getColor() { return color; }
}
public static class Square extends Shape {
protected static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
public Square(int xVal, int yVal, int dim) {
super(xVal, yVal, dim);
color = RED;
}
public void setColor(int newColor) { color = newColor; }
public int getColor() { return color; }
}
public static class Line extends Shape {
protected static final long serialVersionUID=1L;
public Line(int xVal, int yVal, int dim) {
super(xVal, yVal, dim);
color=RED;
}
public void setColor(int newColor) { color = newColor; }
public int getColor() { return color; }
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("/Users/Wei/java/com/ciaoshen/thinkinjava/chapter18/CADState.txt"));
// Read in the same order they were written:
List<Class<? extends Exercise30.Shape>> shapeTypes = (List<Class<? extends Exercise30.Shape>>)in.readObject();
Exercise30.Line.deserializeStaticState(in);
List<Exercise30.Shape> shapes = (List<Exercise30.Shape>)in.readObject();
System.out.println(shapes);
}
}
Exercise 31,32
- Exercise 31: (2) Add appropriate address information to Person.java and People.java.
- Exercise 32: (4) Using a Map<String,Integer> and the net.mindview.util.TextFile utility, write a program that counts the occurrence of words in a file (use “\W+” as the second argument to the TextFile constructor). Store the results as an XML file.
涉及外部库Elliote Rusty Harold的XOM。跳过。
Exercise 33
- Exercise 33: (2) Write a program that displays the current value of a directory called “base directory” and prompts you for a new value. Use the Preferences API to store the value.
package com.ciaoshen.thinkinjava.chapter18;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.prefs.*;
public class Exercise33 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws BackingStoreException{
Preferences root=Preferences.userRoot();
root.clear(); //remove the previous enregistrer
byte[] info=root.getByteArray("base directory","/Users".getBytes());
System.out.println(new String(info));
info="/Users/Wei".getBytes();
root.putByteArray("base directory",info);
System.out.println(new String(root.getByteArray("base directory","/Users".getBytes())));
}
}